Last Update: 10/8/2021

This past weekend The Villiage Seventh-day Adventist Church, in Berrien Springs, Michigan hosted a “COVID Coercion and Conscience” weekend (August 20-21) “With Dr. Peter McCullough – A Nationally Recognized Leader in Early Treatment of COVID-19“.
Dr. Peter McCullough is an American cardiologist. He is former Vice Chief of Internal Medicine at Baylor University Medical Center in Dallas, Texas, and professor at Texas A&M University. He is editor-in-chief of the journals Reviews in Cardiovascular Medicine and Cardiorenal Medicine. While only being 58 years old, he has managed to publish over 650 peer-reviewed papers, which is a real accomplishment.
This past Friday evening (8/20/21), Dr. McCullough started off the weekend with a 1.5-hour talk about the worldwide COVID-19 pandemic, the vaccines against COVID-19, and early treatment protocols (Link). Already, as of 8/22/21, this video has been viewed over 60,000 times! So, the interest is very strong regarding the pandemic we’re in and how to best go about dealing with it. The problem for me is that, while Dr. McCullough did present a few helpful ideas and concepts that are well-supported by empirical evidence, he also made quite a number of key claims that seriously misrepresent the data that is currently in hand. My fear is that the misinformation that Dr. McCullough is effectively spreading will end up hurting many people. So, while I’ve previously addressed a number of McCullough’s mistaken claims along these lines (Link), I’ve decided to review the additional key claims that he presented at the Villiage Seventh-day Adventist Church this past weekend (Link).
Note: This article is fairly long and detailed. For a 5-minute Review / Summary: Link
Table of Contents
- 1 The Vaccines:
- 1.1 A Brand New Technology:
- 1.2 The Spike Protein:
- 1.3 Increase Deaths and Injuries Reported in VAERS:
- 1.4 The Nuremberg Code and Informed Consent:
- 1.5 “Vaccines Don’t Work”:
- 1.5.1 Difference Between Infections and Hospitalizations/Deaths:
- 1.5.2 The Kaiser Permanente Cohort Study:
- 1.5.3 Differences between Pfizer and Moderna Vaccines against Delta Variant:
- 1.5.4 mRNA vaccines more effective than no vaccines against infection:
- 1.5.5 mRNA vaccines still very effective against hospitalizations and death:
- 1.5.6 19% Death Rate for the Vaccinated:
- 1.6 COVID-19 in Pregnancy:
- 1.7 Vaccines Creating a “SuperBug”:
- 1.8 Not a Single Failure of Natural Immunity:
- 1.9 Hard to Transmit the COVID-19 Virus:
- 1.10 The Vaccinated are Killing the Unvaccinated:
- 1.11 Risks of mRNA Vaccines vs. Risks of COVID-19:
- 2 Early Treatment:
- 3 Summary (5-minute read):
- 4 Bio of Dr. Sean Pitman
- 5 Addendum:
The Vaccines:
A Brand New Technology:
Dr. McCullough started off talking about the vaccines that are currently being used against COVID-19 – both RNA- and DNA-based vaccines. He pointed out that these vaccines are a “brand new technology” and that it is impossible to know if these vaccines will be effective, much less safe, given the limited time that they were studied before being brought to the general public worldwide.
The 1976 Sine Flu Fiasco:

As an illustration of the potential for problems, he cited the situation where a vaccine was produced to fight the swine flu (in 1976), noting that just 32 deaths, and some ~500 cases of the rare syndrome Guillain-Barré, out of ~45 million people vaccinated (about 20% of the US population) caused by this vaccine, shut down this vaccine program. He went on to note that “typically over 50 deaths will halt a vaccine in the US”.
As far as the deaths associated with the vaccine at the time, as reported in various new articles, these varied in different reports from 25 to 32. The National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) says that by 22 October 1976, 41 deaths amongst people who had been given the vaccine had been reported by the CDC, but there was “still no known connection to the vaccine” (Link). As is the situation today with the vaccines against COVID-19, deaths without a proven link to the vaccine became the focus of intense media coverage in 1976. Another NCBI article (Link) points to the intense media activity surrounding the death of three elderly people who received the vaccine at the same clinic. Again, however, there was no evidence the deaths were caused by the vaccine. Rather, it seems as though this vaccine program was stopped, not so much because of vaccine-related deaths, but because of the growing number of cases of Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) – a condition that causes paralysis.
The vaccination program was halted in December 1976, days after the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reported a number of cases of GBS among individuals after vaccination. At the time, a consensus was reached that the number of GBS cases was in excess of what would normally be expected, but later research has since found that the chances of developing the condition after vaccination are extremely small (approximately one additional case of GBS for every 100,000 people who got the swine flu vaccine).
[Dr. McCullough] also invokes a comparison beloved of antivaxxers, the 1976 swine flu vaccine, which was associated with a rare incidence of Guillan-Barré syndrome, which is a canard. Basically, antivaxxers claim that the program was killed after 500 cases of Guillain-Barré syndrome and 25 deaths, except that the evidence of association with the vaccine was unclear and there was no transmission of H1N1, leading the CDC to end the program early…
See the difference? In 1976, there was no transmission of H1N1 going on and a question of whether the H1N1 vaccine being used at the time had an association with Guillain-Barré syndrome. Under such circumstances, it was hard to argue for continuing the vaccination campaign. Fast forward 45 years, and we still have widespread community transmission of COVID-19, with the overall death toll approaching 600K in the US alone. It’s an entirely different situation.
Comparison with COVID-19 Vaccinations:
So, how does this compare with the modern vaccines against COVID-19? The VAERS data suggests a possible association with GBS and the Janssen (Johnson and Johnson) vaccine (the number of reported cases of GBS was higher than expected for the “background rate”) at ~7.8 cases per million doses among adults. Currently, however, there is no evidence of increased risk for GBS with the mRNA vaccines. (ACIP Presentation, July 22, 2021)
And, as far as the deaths associated with the vaccines, these are also extremely rare, despite the common misinterpretations of the VAERS database – as discussed further below:
The Origin of mRNA and DNA Vaccine Technology:
 What Dr. McCullough does not clearly explain is that the mRNA technology and other technologies behind the modern vaccines against the COVID-19 virus (to include the DNA-based vaccines) aren’t exactly “new” or “experimental”. They’ve been around and have been carefully studied now for over 30 years! – based largely on the work of Katalin Karikó, Ph.D.
What Dr. McCullough does not clearly explain is that the mRNA technology and other technologies behind the modern vaccines against the COVID-19 virus (to include the DNA-based vaccines) aren’t exactly “new” or “experimental”. They’ve been around and have been carefully studied now for over 30 years! – based largely on the work of Katalin Karikó, Ph.D.
Moderna was founded in 2010 to produce vaccines based on the new mRNA technology, and the company had been growing as a vaccine manufacturer when the COVID-19 virus became a pandemic early in 2020. BioNTech is a German company established to work on immunotherapies in 2008 by a Turkish couple, who immigrated to Germany. Like Moderna, BioNTech recognized the value of the mRNA technology for vaccine design years ago and licensed the technology. In 2013, BioNTech hired Karikó as a vice president and began to develop mRNA technologies for use against many diseases. BioNTech’s efforts in vaccine development greatly increased in 2018, when Pfizer joined BioNTech’s effort with a research and development agreement to develop mRNA-based vaccines against influenza. It was a natural collaboration because Pfizer, a U.S. company in New York, has been a major vaccine producer for a long time. When the pandemic began, Pfizer/BioNTech immediately turned their attention to developing vaccines against COVID-19. (Link, Link)
It’s not like there’s some deep mystery here as to how they fundamentally work. We know very well how they work (Link). And, Dr. McCullough is not against vaccines in general. He has taken dozens of vaccines himself – as he freely admits. So, what’s his real problem with the vaccines against COVID-19? Well, it’s his fear of the “spike protein”. He also throws in some possibilities of some future “cancer risk” or “birth defects”, but doesn’t explain why such risks wouldn’t have been detected well before now – given the 70,000 people involved in the original double-blinded placebo-controlled trials (not to mention the animal trials, or the hundreds of millions of people who have since been vaccinated). He does say that such risks usually require “two years” before they can be effectively ruled out for a new vaccine. However, his primary concern seems to be with the spike protein produced by the vaccines.
Comparison with Patisiran mRNA to Treat ATTR:
 Patisiran, sold under the brand name Onpattro, is a medication for the treatment of polyneuropathy in people with hereditary transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis (first used in 2017). Hereditary transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis is a fatal rare disease that is estimated to affect 50,000 people worldwide. The per-patient cost is between $451,000 and $677,000 per year, depending on the number of vials needed (Link, Link)
Patisiran, sold under the brand name Onpattro, is a medication for the treatment of polyneuropathy in people with hereditary transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis (first used in 2017). Hereditary transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis is a fatal rare disease that is estimated to affect 50,000 people worldwide. The per-patient cost is between $451,000 and $677,000 per year, depending on the number of vials needed (Link, Link)
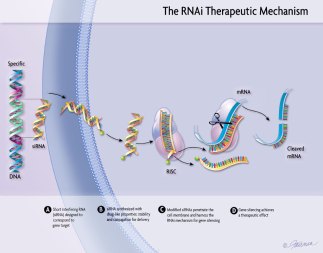 So, why do I bring this up? Because, Patisiran is based on the very same mRNA technology used in the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines. It uses lipid nanoparticles to deliver specially coded mRNA into human cells to produce the desire protein sequences to treat disease. About 1,000 people have been using Pitisiran since 2017. Now, the mRNA vaccines against COVID-19 use two injects of 30μg (Pfizer) to 100μg (Moderna) of mRNA for each injection. In comparison, Patisiran uses around 100x this dose of mRNA, which gets injected intravenously every three months . . . indefinitely since 2017. And, this was done with good safety as well as efficacy results (Link).
So, why do I bring this up? Because, Patisiran is based on the very same mRNA technology used in the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines. It uses lipid nanoparticles to deliver specially coded mRNA into human cells to produce the desire protein sequences to treat disease. About 1,000 people have been using Pitisiran since 2017. Now, the mRNA vaccines against COVID-19 use two injects of 30μg (Pfizer) to 100μg (Moderna) of mRNA for each injection. In comparison, Patisiran uses around 100x this dose of mRNA, which gets injected intravenously every three months . . . indefinitely since 2017. And, this was done with good safety as well as efficacy results (Link).
See also the discussion of Patisiran by Dr. Steve Lee: Link
The Spike Protein:
 The main fear of Dr. McCullough, when it comes to the vaccines against the COVID-19 virus, all boils down to the “spike protein” that is produced by these vaccines. Spike proteins are found on all coronaviruses, not just the SARS-CoV-2 virus. For example, the “common cold” is caused by coronaviruses (such as HCoV-229E). And, they all have “spike proteins” on their surfaces. And, most of us do just fine when it comes to making it through a common cold. So, what’s so bad about the SARS-CoV-2 spike proteins that have been used as “targets”? – as the product of the modern vaccines against COVID-19?
The main fear of Dr. McCullough, when it comes to the vaccines against the COVID-19 virus, all boils down to the “spike protein” that is produced by these vaccines. Spike proteins are found on all coronaviruses, not just the SARS-CoV-2 virus. For example, the “common cold” is caused by coronaviruses (such as HCoV-229E). And, they all have “spike proteins” on their surfaces. And, most of us do just fine when it comes to making it through a common cold. So, what’s so bad about the SARS-CoV-2 spike proteins that have been used as “targets”? – as the product of the modern vaccines against COVID-19?
Well, according to Dr. McCullough, these particular spike proteins of SARS-CoV-2 were deliberately manipulated and design, by laboratory scientists, specifically to infect and kill people. In other words, Dr. McCullough believes that these particular spike proteins were not naturally produced, but were produced by humans as a type of bioweapon. What evidence does he have for this? He doesn’t say…
What he does say is that this extremely harmful and dangerous spike protein is not only produced at the site of vaccine injection (according to the information coded by the vaccine’s DNA and/or RNA that was “made to last” longer than natural RNA or DNA sequences), but that this spike protein, once produced, goes throughout the body causing damage to every organ in the body – to include the heart, brain, adrenal glands, and ovaries in particular. He claims that the spike proteins can “circulate in the body for between 2 weeks and 9 months – and can even be passed on from one cell to “daughter cells” after cell division.
The Japanese “Biodistribution Study”:
 If true, this all sounds very scary indeed! So, what evidence does Dr. McCullough offer to back up these scary claims? Well, he starts off by citing a “biodistribution study” obtained from the Japanese Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (Link, Link in English). He said the study shows how the coronavirus spike protein circulates in the bloodstream of vaccinated individuals and accumulates in their organs. First off, however, this particular study didn’t deal with the spike proteins at all, only with the distribution of lipid nanoparticles – which Dr. McCullough alludes to via a very quick reference to “nanoparticles”, but without explaining that these nanoparticles are tiny lipid droplets used in vaccine transport – not the spike proteins produced by the vaccines at the site of injection.
If true, this all sounds very scary indeed! So, what evidence does Dr. McCullough offer to back up these scary claims? Well, he starts off by citing a “biodistribution study” obtained from the Japanese Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (Link, Link in English). He said the study shows how the coronavirus spike protein circulates in the bloodstream of vaccinated individuals and accumulates in their organs. First off, however, this particular study didn’t deal with the spike proteins at all, only with the distribution of lipid nanoparticles – which Dr. McCullough alludes to via a very quick reference to “nanoparticles”, but without explaining that these nanoparticles are tiny lipid droplets used in vaccine transport – not the spike proteins produced by the vaccines at the site of injection.
“The document is a real (common technical document), though it’s not leaked – it’s part of the submission data applied by Pfizer to PMDA (Japan’s version of FDA) for its review,” Kit Longley, senior manager of science media relations, said in an email. “The document is about the pharmacokinetics overview seen from lab studies and we can confirm it’s not about spike proteins from the vaccine resulting in dangerous toxins that linger in the body.” (Link)
Beyond this, Dr. McCullough doesn’t seem to understand what the paper is actually saying about the distribution of the lipid nanoparticles from the vaccines either.
Vaccine Lipid Nanoparticles Accumulate in the Ovaries of Women:
The common claim (among anti-vaxxers and Dr. McCullough lately) that lipid nanoparticles from the mRNA vaccines accumulate specifically in the ovaries of women, producing infertility, is also based on this same Japanese Biodistribution Study. However, the way this claim is presented, and the implications suggested by Dr. McCullough, are inaccurate and very misleading.
The biodistribution study found that the injection site retained the highest concentration of lipid nanoparticles, not the ovaries.
This data was obtained by injecting rats with a mix of lipid nanoparticles, which are identical to the ones used in the COVID-19 RNA vaccines, that carry a radioactive “label” (deuterium). Researchers then then measured the level of radioactivity in tissues at different time points after injection. The level of radioactivity acts as a proxy measurement for how much lipid nanoparticle is present in a given tissue. Changes in the level over time provide scientists with an idea of how long it takes for the body to eliminate the particles.
The article’s interpretation of the biodistribution data is inaccurate. As Abraham Al-Ahmad, an associate professor in pharmacology at Texas Tech University, pointed out in a blog post, the data showed that the injection site had the greatest accumulation of lipid nanoparticles, followed by the liver. Specifically, the peak concentration at the injection site was 52.6% of the administered dose at one hour post-injection. That of the liver was 18.1% of the administered dose at eight hours post-injection (see Table 1). A microgram is one-millionth of a gram.
However, instances of this claim, as seen in the TrialSite News article, tend to omit the table containing the data for the liver and injection site, instead drawing attention only to the data for the ovaries.
The peak concentration in the ovaries, occurring at 48 hours post-injection, was just 0.095% of the administered dose (see Table 2). [or less than 1:1,000 of the total dose of lipid nanoparticle. 50% was metabolized by liver. Brain peak was 0.02% (1/5000 of the total dose)]
Apart from the inaccurate interpretation of data, another critical aspect of the biodistribution experiment that TrialSite News failed to consider is the amount of lipid nanoparticles administered in the rats and its relevance, or more precisely, its lack thereof to the amount present in RNA vaccines given to people.
The study administered 50 micrograms of lipid nanoparticles to each rat. As explained by David Gorski, a professor of surgery at Wayne State University and editor of Science Based Medicine, this would effectively translate to a much higher dose in rats than in humans [a does of ~18-35x higher than the typical adult human dose]. This is due to the large difference in body weight:
In other words, the dose administered to rats was far higher than the dose used in people. There isn’t evidence showing that COVID-19 RNA vaccines are causing fertility problems.
Source of Claim: Steve Kirsch, TrialSite News, 25 May 2021
Rebuttle of Claim: HealthFeedback.org – 24 Jun 2021 | Editor: Flora Teoh
Also, why would lipid nanoparticles (tiny fat droplets) be harmful to the human body? The fats that we eat are absorbed and generally distributed and used throughout the body as well – without any problems. What is so concerning about the lipid droplets used in the mRNA vaccines? Where is the evidence that they would or could cause any negative effects on the ovaries? – or any other organ system within the human body?
There have been actual studies of COVID-19 vaccines and ovarian function. In one such study, for example, researchers studied women undergoing oocyte retrieval for in vitro fertilization. They found no detrimental effect on ovarian follicular function. Another study of women undergoing in vitro fertilization demonstrated that the Moderna COVID-19 vaccine has no detectable effect on the percentage of clinical pregnancies resulting from the procedure. Yet another study has shown that vaccination against COVID-19 has no effect on immunological tolerance of the fetus by the mother. Still another study failed to find any effect on embryo implantation rates between SARS-CoV-2 infection seropositive, SARS-CoV-2 vaccine seropositive, or seronegative women. (Link)
Scientists at the University of Guelph’s Ontario Veterinary College also say that McCullough’s claims are completely wrong here.
“The bottom line is the vaccine contains an altered protein that is designed to prevent full activation, and it circulates for a short period of time at levels that are far below what would be a concern,” W. Glen Pyle, a professor in the Department of Biomedical Sciences, said in an email.
J. Scott Weese, an associate professor in the Department of Pathobiology, said in an email that all evidence suggests the coronavirus vaccines are safe. Misinformation about the safety of the vaccines appears to be aimed at “creating fear and confusion during a critical time in this pandemic,” he said.
“The efficacy and safety of mRNA vaccines is astounding, to me, particularly for a virus we’ve only known for a year and a half,” Weese said. “mRNA vaccines have been used on millions of people, including extremely high rates of vaccination in high-risk populations (elderly, patients with other diseases), with incredibly low adverse event rates.” (Link)
Very Few Spike Proteins Make it to Bloodstream:
Again, the basic facts here are that the vast majority of the spike proteins produced by the vaccines against the COVID-19 virus remain local at the injection site. Very few make it to the bloodstream, and those that do circulate in the bloodstream are not toxic because of three reasons:
- There just aren’t enough of them to produce toxicity.
- The few spike proteins that do make it into the blood are almost all filtered out by the liver.
- The spike proteins produced have been modified to reduce bioactivity within the body.
Some of the vaccine dose is going to make it into the bloodstream, of course. But keep in mind, when the mRNA or adenovirus particles do hit cells outside of the liver or the site of injection, they’re still causing them to express Spike protein anchored on their surfaces, not dumping it into the circulation. Here’s the EMA briefing document for the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine – on pages 46 and 47, you can read the results of distribution studies. These were done two ways – by using an mRNA for luciferase (and thus looking at the resulting light emission from the various rodent regions!) and by using a radioactive label (which is a more sensitive technique). The great majority of the radioactivty stays in and around the injection site. In the first hours, there’s also some circulating in the plasma. But almost all of that ended up in the liver, and no other tissue was much over 1% of the total…
In the Moderna, Pfizer/BioNTech, J&J, and Novavax vaccines, the Spike protein has some proline mutations introduced to try to hold it in its “prefusion” conformation, rather than the shape it adopts when it binds to ACE2. So that should cut down even more on the ability of the Spike protein produced by these vaccines to bind and produce the effects noted in the recent papers. (Derek Lowe, May 4, 2021)
The S1 protein started showing up as early as the first day after vaccination, peaked at around day 5, and was undetectable by day 14… The mRNA from the vaccine starts being picked up and translated into protein almost immediately, as is clear from the quick detection of S1 protein. That’s there because it’s been cleaved off the full Spike protein, but the reason that the Spike itself isn’t found (at least at the limits of detection in the assay, and it’s a really good assay) is because it’s bound to the cells where it’s produced, by the transmembrane anchor region (discussed in that earlier post I referenced above). The reason that no S1 protein is found after the second vaccination is clear – by then, a robust antibody response to it has had a chance to develop, and the protein gets rapidly cleared from the blood, just like it’s supposed to…
It seems clear from all these human trials and the clinical experience to date that the circulating levels of the S1 protein (or the Spike itself) that are sufficient to induce a protective immune response are not in themselves toxic. The animal studies demonstrate that the Spike or S1 can indeed have bad effects on living cells and tissues all by themselves, but the conditions under which this was demonstrated are not those that obtain after vaccination.
And this latest paper showing circulating S1 protein after vaccination? Coupled with the previous paper from the same group, it in fact provides strong evidence that such blood levels are not by themselves the cause of coronavirus symptoms and tissue damage. No, if you want to try for severe, permanent damage, you will need to get infected by real SARS-CoV-2 itself and take your chances. Try your luck, if you like, with the short-term symptoms and with “long Covid” symptoms as well. See if you stay out of the ICU, or if you retain your sense of smell – try them all. If you would rather not spin that wheel, and you shouldn’t, then my strong, heartfelt advice is to get vaccinated. Because then you will be protected.
In short, this claim simply isn’t based on what most medical scientists would call reasonable information.
Increased Rate of Miscarriage in Humans and Animals following Vaccination:
Still, Dr. McCullough argues that the Japanese Biodistribution Study (discussed above) is supported by evidence for increased miscarriages in humans as well as in animal studies.
That’s another very scary claim, if true. So, upon what is this claim based?
Placental Syncytin-1 Protein:
 Well, a widely shared petition (December 1, 2020) from Michael Yeadon (a former scientific researcher and vice president at Pfizer Inc.), claimed the coronavirus’s spike protein contained within the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines was similar to a protein called syncytin-1, involved in forming the placenta. He speculated that this might cause antibodies against the virus to attack a developing pregnancy, too.
Well, a widely shared petition (December 1, 2020) from Michael Yeadon (a former scientific researcher and vice president at Pfizer Inc.), claimed the coronavirus’s spike protein contained within the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines was similar to a protein called syncytin-1, involved in forming the placenta. He speculated that this might cause antibodies against the virus to attack a developing pregnancy, too.
Some experts believe this was the origin of the whole belief that Covid vaccines might harm fertility (Link). In reality, however, syncytin-1 and the coronavirus’s spike protein are just about as similar as any two random proteins – so there really is no good reason to believe the human immune system might confuse them, to begin with. And, as far as I’m aware, no published data have shown any problems with human fertility or an increase in miscarriages following vaccination. On the contrary, studies have also been done showing the miscarriage rate among vaccinated people was in line with the rate expected in the general population – 12.5%. (Shimabukuro, June 17, 2021)
But what about the animal studies cited by Dr. McCullough? Well, they show the opposite of what McCullough claimed in his talk.
There were no effects of BNT162b2 [Pfizer] on female [rats] mating performance, fertility, or any ovarian or uterine parameters nor on embryo-fetal or postnatal survival, growth, physical development or neurofunctional development in the offspring through the end of lactation (Bowman, et. al., May 28, 2021).
Increase Deaths and Injuries Reported in VAERS:
 As usual, Dr. McCullough put a great deal of emphasis on the VAERS reporting system (Vaccine Adverse Events Reporting System – maintained by the CDC and the FDA), noting that over 12,000 deaths had been reported to VAERS following vaccination against COVID-19 (as of July 30, 2021) with 40% of these deaths occurring within 3 days of vaccination – compared with a usual rate of just 155 reported deaths annually. He notes that this sudden spike in reported deaths in the VAERS system has “never been seen in medicine”. In a previous talk, he argued that this is likely an underreport of the true number of deaths following vaccination by a factor of 10 (Link). In other words, Dr. McCullough believes that the COVID-19 vaccines are likely responsible for over 120,000 deaths so far – calling it one of the worst national disasters ever. He claims that his interpretation of this data is so obvious that those doctors and scientists who have published papers saying that these features of VAERS are “not related to the vaccines” are committing “malfeasance” – or intentional conduct that is wrongful or unlawful.
As usual, Dr. McCullough put a great deal of emphasis on the VAERS reporting system (Vaccine Adverse Events Reporting System – maintained by the CDC and the FDA), noting that over 12,000 deaths had been reported to VAERS following vaccination against COVID-19 (as of July 30, 2021) with 40% of these deaths occurring within 3 days of vaccination – compared with a usual rate of just 155 reported deaths annually. He notes that this sudden spike in reported deaths in the VAERS system has “never been seen in medicine”. In a previous talk, he argued that this is likely an underreport of the true number of deaths following vaccination by a factor of 10 (Link). In other words, Dr. McCullough believes that the COVID-19 vaccines are likely responsible for over 120,000 deaths so far – calling it one of the worst national disasters ever. He claims that his interpretation of this data is so obvious that those doctors and scientists who have published papers saying that these features of VAERS are “not related to the vaccines” are committing “malfeasance” – or intentional conduct that is wrongful or unlawful.
Dr. McCullough is also shockingly ignorant of how VAERS works. He claims that only a health care worker can access the system and that a patient or a loved one has to contact a physician or health care worker to enter a report. That is completely wrong. Indeed, one of the complaints about VAERS is that anybody—and I do mean anybody—can enter a report. It is this openness that is simultaneously one of VAERS greatest strengths and weaknesses. It’s a weakness in that this openness allows for gaming of the system, as lawyers for parents seeking to sue vaccine manufacturers for autism as a “vaccine injury” did 15 years ago. Seriously, this is an error huge enough to make me wonder about everything else, in particular whether he got his MPH out of a cereal box. This guy has an MPH and doesn’t know (or didn’t bother to find out) how VAERS actually works and that there are other vaccine safety monitoring systems other than VAERS?
How VAERS works:
 This sounds horrible! How could the government be allowing this sort of catastrophe to be happening in this country?! Well, things aren’t always as they may seem on the surface – even for a doctor like Dr. McCullough. It has to do with the nature of the VAERS reporting system. People can report anything to VAERS without any kind of demonstration of a causal link to a vaccine or anything else. The fact of the matter is that even if I were to simply wave my hand over the foreheads of a population the size of the United States that nearly 8,000 people would die that very same day (Link). So, it only stands to reason that, out of the 178 million Americans who have currently received at least one dose of a vaccine against COVID-19 (54%) that many tens of thousands of people would have died, for various reasons, within three days of being vaccinated. Here’s another commentary to illustrate this point:
This sounds horrible! How could the government be allowing this sort of catastrophe to be happening in this country?! Well, things aren’t always as they may seem on the surface – even for a doctor like Dr. McCullough. It has to do with the nature of the VAERS reporting system. People can report anything to VAERS without any kind of demonstration of a causal link to a vaccine or anything else. The fact of the matter is that even if I were to simply wave my hand over the foreheads of a population the size of the United States that nearly 8,000 people would die that very same day (Link). So, it only stands to reason that, out of the 178 million Americans who have currently received at least one dose of a vaccine against COVID-19 (54%) that many tens of thousands of people would have died, for various reasons, within three days of being vaccinated. Here’s another commentary to illustrate this point:
There were 293 deaths reported to VAERS during the last week of April. That sounds like a large number, particularly when, averaged out, it translates to 41.9 deaths per day. But is it? How many people received COVID-19 vaccines that week? By subtracting the April 23 statistic from the April 30 statistic, I come up with 7.66 million people receiving a COVID-19 vaccine during the last week of April, or 1.1 million/day. How many deaths would we expect in a week in a population of 7.66 million in a week, based on the CDC’s pre-pandemic statistics? Using the aforementioned yearly incidence of death pre-pandemic of 868.7 per 100,000 in a year, we can say that in a population of that size there would be 66,619 deaths in a year, or 182.5 deaths per day or 1,278 deaths in a week… Think of it this way. Never before in the history of VAERS has there been a mass vaccination program like that for COVID-19. The population initially targeted vaccination was exactly the population that has the highest baseline death rate, meaning that by random chance alone we would expect to see a seemingly large number of deaths within days of vaccination.
But there’s yet another factor. Those who have received a COVID-19 vaccination know that all those who receive COVID-19 vaccines are given instructions to sign up for V-Safe, a monitoring system that works by text message. Basically, if you sign up for V-Safe, you will receive periodic text messages, starting as daily text messages that become less frequent over time. I note that, even though I completed my vaccination series in January, I still receive V-Safe texts periodically. This basically turns a passive surveillance system into a quasi-active surveillance system. And, remember, the more you look for something, the more you will find. Always.
The law of large numbers says that, whenever an intervention is administered to huge numbers of people, there will be large numbers of adverse events that happen after that intervention by random chance alone. The way scientists determine if there is a safety signal in those adverse events is by comparing them to the expected baseline rate of each adverse event. The bottom line is that, fear mongering articles by RFK Jr. and reports of a “vaccine Holocaust” to the contrary, there is no evidence of deaths above and beyond what one would expect based on known baseline rates of death in the US population. Although RFK Jr. might not be expected to know this, someone like Dr. McCullough, who has an MPH in addition to his MD, should really, really, really know better. That he promotes antivaccine disinformation based on fear mongering about reports to VAERS of deaths and adverse events tells me one of two things. Either his MPH education failed him, or he’s lying. Take your pick. .
So, for Dr. McCullough to claim that the vaccines are clearly responsible for deaths reported to VAERS following vaccination is clearly misguided. The fact is that he has no evidence whatsoever that the vaccines were responsible for these deaths. Rather, the intended purpose of VAERS is to detect patterns that occur above and beyond normal background levels for large populations – like the US population. And, so far, the vaccines against COVID-19 have proven themselves to be not only very effective against COVID-19, but also very safe. While some serious risks have been detected, these risks are very rare (Link).
 But what about the graph shown by Dr. McCullough that demonstrated a dramatic increase in the number of deaths reported to VAERS since the beginning of vaccinations against COVID? After all, the usual number of deaths reported to VAERS is less than 200 per year. Why, all of a sudden, is there a spike of reported deaths to VAERS in 2021 of over 5,000 deaths? Well, this could be for a number of reasons (as Dr. Gorski pointed at above). It could be that the worldwide nature of the COVID-19 pandemic and the strong promotion of the vaccines to help fight it simply makes people much more aware and vigilant when it comes to events surrounding vaccines against COVID-19. Everyone is aware of the situation we’re in and all of the unusual restrictions. This issue has become very political instead of just a medical/scientific question – and has become very divisive as a result. It is no wonder, then, that there has been a sudden increase in reported deaths to VAERS following the COVID-19 vaccinations in particular. The very consistent V-Safe Texts also contribute to this heightened awareness for those who’ve been vaccinated. However, this doesn’t prove or even suggest, by itself without additional evidence, a correlation with the vaccines. After all, the very same type of thing has happened before. Note that during the H1N1 flu outbreak in 2009 that there was also a spike in VAERS reporting that went well above the expected background death rate.
But what about the graph shown by Dr. McCullough that demonstrated a dramatic increase in the number of deaths reported to VAERS since the beginning of vaccinations against COVID? After all, the usual number of deaths reported to VAERS is less than 200 per year. Why, all of a sudden, is there a spike of reported deaths to VAERS in 2021 of over 5,000 deaths? Well, this could be for a number of reasons (as Dr. Gorski pointed at above). It could be that the worldwide nature of the COVID-19 pandemic and the strong promotion of the vaccines to help fight it simply makes people much more aware and vigilant when it comes to events surrounding vaccines against COVID-19. Everyone is aware of the situation we’re in and all of the unusual restrictions. This issue has become very political instead of just a medical/scientific question – and has become very divisive as a result. It is no wonder, then, that there has been a sudden increase in reported deaths to VAERS following the COVID-19 vaccinations in particular. The very consistent V-Safe Texts also contribute to this heightened awareness for those who’ve been vaccinated. However, this doesn’t prove or even suggest, by itself without additional evidence, a correlation with the vaccines. After all, the very same type of thing has happened before. Note that during the H1N1 flu outbreak in 2009 that there was also a spike in VAERS reporting that went well above the expected background death rate.
During the period from 1 July 2010 to 6 May 2016 following the 2009 H1N1 influenza pandemic, 671 reports after influenza vaccines in pregnant women were submitted to VAERS; 544 were after IIV. This represents a decrease in the annual number of pregnancy reports following the 2009 H1N1 pandemic (Fig. 1) despite similar vaccination coverage as observed during the pandemic year, but an increase over the period 1990 – 2009 before the H1N1 pandemic. Prior to the 2009 H1N1 pandemic, pregnancy reports after IIV had been sparsely reported to VAERS. The peak in the number of pregnancy reports observed during 2009 – 2010 followed by a decrease in reporting suggests that the 2009 spike in pregnancy reports after 2009 H1N1 inactivated vaccines may have been due to stimulated reporting. During the current review, we did not observe any new AE or condition of concern. Moreover, data mining analysis did not reveal any disproportionate reporting for any pregnancy-specific MedDRA®PT. (Link)
This is what a lot of people don’t understand – including some of those with an M.D. or a Ph.D. behind their names. There is a world of difference between causation and correlation. And, sometimes, it can be very hard to tell the difference. That is why very careful scientific studies and investigations are required to determine if there is, or isn’t, a true connection between two events.
Dr. Jessica Rose and the Clustering of VAERS Reports:
 But what about the paper by Dr. Rose that Dr. McCullough mentioned in his talk? – presenting the problems that the VEARS data so clearly shows for the vaccines (Rose, May 2021)?
But what about the paper by Dr. Rose that Dr. McCullough mentioned in his talk? – presenting the problems that the VEARS data so clearly shows for the vaccines (Rose, May 2021)?
Using vaccine data up to April 10, 2021, Dr. Rose noted that by the end of March, about 100X more COVID-19 vaccinations occurred as opposed to flu vaccinations. This was associated with 380 times more safety reports due to COVID-19 vaccinations. This means that 99% of all adverse events (AEs) currently recorded in VAERS are associated with the mass COVID-19 vaccination program. Beyond this, Dr. Rose makes the same argument as Dr. McCullough – that the clustering of deaths near the day of vaccine exposure means that the vaccines must have been responsible for these deaths.
Dr. Rose was independently following up on a challenge, published on social media, to find that the number of deaths was not evenly distributed across the days following vaccination – which would suggest a non-causal relationship. Since she found that the reported distribution is not evenly distributed, her conclusion follows that, therefore, this uneven distribution is, in fact, causal. In other words, that the vaccines are, in fact, associated with the death reported to VAERS.
 So, is this true? Is the non-linearity of the reporting of deaths to VAERS following vaccination supportive of the conclusion that these deaths were caused by the vaccine? – even if these deaths are not increased beyond what would normally be expected? – as in the number of deaths expected from a saline injection or me waving my hand over the foreheads of 100 million people?
So, is this true? Is the non-linearity of the reporting of deaths to VAERS following vaccination supportive of the conclusion that these deaths were caused by the vaccine? – even if these deaths are not increased beyond what would normally be expected? – as in the number of deaths expected from a saline injection or me waving my hand over the foreheads of 100 million people?
First, let’s ask the question as to the deaths reported in the 70,000 people who originally signed up for the mRNA double-blinded placebo-controlled trials (Pfizer and Moderna combined). Now, six participants died during the 44,000 person Pfizer vaccine trial, two of whom were given the vaccine while the other four people received a placebo. Of the two vaccine recipients who died, one had a cardiac arrest 62 days after a second dose of the two-dose vaccination and died three days later, while the other died from arteriosclerosis three days after a first dose of the vaccination. One of the placebo recipients died from myocardial infarction, another from hemorrhagic stroke, and two others from unknown causes. It was similar for the Modern study. Three vaccinated participants died during the study while four died in the placebo group, for a total of 7 deaths (by the cutoff date of November 11, 2020).
Now, if the mRNA vaccines were so lethal, given the conclusions of Dr. Rose and Dr. McCullough here, why wasn’t this pattern detected in the original vaccine trials for Pfizer and/or Moderna? Why, did this pattern not turn up until there was a spike in VAERS reporting? Also, why is the death rate among the vaccinated not actually spiking above expected background levels? – especially given the severity of the problem according to Dr. McCullough? I mean, with upwards of 120,000 deaths caused by vaccines in the US, you would think this would also be reflected in an increase in the death rate among those who are vaccinated that is above the expected background levels within various age categories. Where is this evidence?
I’m sorry, but it seems far more likely that the VAERS reporting spike, to include the tendency to favor reporting closer to the vaccination event, is due to the significant increase in awareness that has been associated with this pandemic – worldwide. And, this conclusion is backed up by the research study of Klein et al., (September 3, 2021) into this question. An interim analysis of 6.2 million individuals who received more than 11.8 million doses of the mRNA COVID-19 vaccines revealed no significant link between the vaccines and serious adverse events, and no clustering of adverse events close to the time of vaccination, according to researchers:
In this interim analysis of surveillance data from 6.2 million persons who received 11.8 million doses of an mRNA vaccine, event rates for 23 serious health outcomes were not significantly higher for individuals 1 to 21 days after vaccination compared with similar individuals at 22 to 42 days after vaccination.
Klein et al., September 3, 2021
The results, published in JAMA, showed that the risk vs. comparison intervals for incidence of ischemic stroke was 1,612 vs. 1,781 per 1 million person-years (RR = 0.97; 95% CI, 0.87-1.08); appendicitis was 1,179 vs. 1,345 per 1 million person-years (RR = 0.82; 95% CI, 0.73-0.93); and acute myocardial infarction was 935 vs. 1,030 per 1 million person-years (RR = 1.02; 95% CI, 0.89-1.18). The incidence of confirmed anaphylaxis was 4.8 (95% CI, 3.2-6.9) per 1 million Pfizer-BioNTech doses and 5.1 (95% CI, 3.3-7.6) per 1 million Moderna doses. (Link)
Dr. Tess Lawrie and the UK’s Yellow Card Program:
 Dr. McCullough then goes on to cite the work of Dr. Tess Lawrie (also a big proponent of ivermectin use for COVID-19 – see below) regarding the “Yellow Card Program” in England that is very similar to the VAERS program in the US.
Dr. McCullough then goes on to cite the work of Dr. Tess Lawrie (also a big proponent of ivermectin use for COVID-19 – see below) regarding the “Yellow Card Program” in England that is very similar to the VAERS program in the US.
The Yellow Card scheme (similar to the Vaccine Adverse Events Reporting System in the U.S.) can be added to by anyone, whether a clinician or a member of the public. The scheme aims to help regulators identify potential side effects involving medicines or vaccines that had not been detected or are more common than seen in clinical trials.
Consider the following review from Ian Le Guillou (HealthFeedback.org, June 16, 2021):
However, the figures reported through the scheme are not sufficient to establish a proven side effect. The U.K.’s Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA), which runs the Yellow Card scheme, says:
“The nature of Yellow Card reporting means that reported events are not always proven side effects. Some events may have happened anyway, regardless of vaccination. This is particularly the case when millions of people are vaccinated, and especially when most vaccines are being given to the most elderly people and people who have underlying illness.”
In other words, it may simply be a coincidence that an adverse event, such as a cancer diagnosis or a speech disorder, happened within a short period after vaccination. Detailed analysis is needed to understand whether an adverse event happens at a higher rate than would be expected in the population.
The director of The Evidence-Based Medicine Consultancy Ltd, Tess Lawrie, wrote to the head of the MHRA about the adverse events reported for the COVID-19 vaccines. In the letter, which was quoted heavily in the article on America’s Frontline Doctors, Lawrie said that she would “like to draw your attention to the high number of covid-19 vaccine-attributed deaths”. However, as previously explained, deaths or any adverse events reported through the Yellow Card scheme were not attributed to vaccination.
In the letter, Lawrie stated that she recognized the limitations of the data and understood “that information on reported Adverse Drug Reactions should not be interpreted as meaning that the medicine in question generally causes the observed effect or is unsafe to use.” However, she contradicted this by concluding:
“The MHRA now has more than enough evidence on the Yellow Card system to declare the COVID-19 vaccines unsafe for use in humans.”
As evidence for her statements, Lawrie cited the numbers of various adverse events identified through the Yellow Card scheme. However, these reports can’t be used to establish a causal relationship between the vaccine and the occurrence of an adverse event. In addition, the raw numbers lack the context necessary to establish whether the vaccines are safe for use or not. Among the factors to consider are the expected side effects from vaccination, adverse events that would have happened regardless of vaccination, and the benefits of vaccination.
Expected side effects
The figures used by Lawrie overlook the fact that most of the reported adverse events are minor and transient, consisting of expected immune system responses associated with the use of vaccines. For instance, almost half of the nervous system disorders reported were headaches, which is listed as a very common side effect of the vaccines. There are also many reports of other common side effects such as pain, nausea, fever, and fatigue. The MHRA website clarified:
“For all vaccines, detailed review of all reports has found that the overwhelming majority relate to injection site reactions (sore arm for example) and generalised symptoms such as a ‘flu-like’ illness, headache, chills, fatigue (tiredness), nausea (feeling sick), fever, dizziness, weakness, aching muscles, and rapid heartbeat. Generally, these happen shortly after the vaccination and are not associated with more serious or lasting illness. These types of reaction reflect the acute immune response triggered by the body to the vaccines, are typically seen with most types of vaccine and tend to resolve within a day or two.”
Expected adverse events in the population
About 40 million people in the U.K. have received at least one dose of a COVID-19 vaccine since December 2020. Among such a large group of people, we would naturally expect to observe many medical conditions to arise that would have happened regardless of vaccination. The numbers reported through the Yellow Card Scheme do not provide this context, which would be necessary to determine whether an adverse event is occurring at an increased rate. The MHRA said:
“The total number and the nature of Yellow Cards reported so far is not unusual for a new vaccine for which members of the public and healthcare professionals are encouraged to report any suspected adverse reaction.”
Benefits of the vaccine
Each drug or vaccine is expected to cause a certain degree of side effects. However, this is weighed against the benefits of such an intervention to establish whether the public should use it. Lawrie does not appear to consider the benefits of vaccination in reducing deaths and hospitalizations due to COVID-19. The MHRA said:
“The expected benefits of the vaccines in preventing COVID-19 and serious complications associated with COVID-19 far outweigh any currently known side effects. As with all vaccines and medicines, the safety of COVID-19 vaccines is continuously monitored and benefits and possible risks remain under review.”
The Yellow Card scheme and its equivalents in other countries have already shown their use in identifying rare adverse events that may be linked to vaccinations. Regulators investigated following reports of an extremely rare specific type of blood clot in the brain, known as cerebral venous sinus thrombosis, occurring together with low levels of platelets (thrombocytopenia). Investigations found evidence for an increased risk of these rare blood clots among younger people after receiving the AstraZeneca vaccine. This led to many countries changing the vaccination guidelines, preferring an alternative COVID-19 vaccine for younger people.
Similarly, rare occurrences of anaphylaxis (a severe allergic reaction) also led to changes in guidance and information on the choice of vaccines for susceptible individuals.
In summary, the reports identified by Lawrie do not indicate any unexpected side effects from the COVID-19 vaccines. The Yellow Card scheme does not assign a cause to medical events following vaccination. The MHRA regulatory body collects this data to prompt further investigation if they have concerns. The MHRA analyzed the data and confirmed that the benefit of the COVID-19 vaccines “far outweigh any currently known side effects”.
See also the very recent results for a very large study showing the significant reduction in risk for those who are vaccinated with Pfizer vs. those who come done with a COVID-19 infection (Barda, et. al., August 25, 2021) as well as further discussion in this article here: Link
Dr. Scott McLachlan and 86% Post-Vaccine Deaths in VAERS:
 Dr. McCullough also highlights a preprint paper published by Dr. McLachlan (McLachlan et. al., June 2021) where the authors point out that, “There were only 14% of the cases [in the VAERS database] for which a vaccine reaction could be ruled out as a contributing factor in their death. Given this comment, Dr. McCullough’s headlines that “86% of deaths in VAERS have no other explanation other than being caused by the vaccines”.
Dr. McCullough also highlights a preprint paper published by Dr. McLachlan (McLachlan et. al., June 2021) where the authors point out that, “There were only 14% of the cases [in the VAERS database] for which a vaccine reaction could be ruled out as a contributing factor in their death. Given this comment, Dr. McCullough’s headlines that “86% of deaths in VAERS have no other explanation other than being caused by the vaccines”.
But how do we actually know this? Even the paper’s abstract says that only 67% of the cases were reported by medical personnel. Even here, however, aside from the proximity of the death to the vaccination event, what other evidence is there to conclude that the vaccine was responsible for these deaths? – especially given that these deaths are not above the expected number of deaths if only saline injections were given? or a wave of the hand over the forehead? It’s not like medical providers somehow enhance the VAERS reports because of their medical knowledge. “After someone receives a COVID-19 vaccine, their healthcare provider is required by law to report all serious adverse health events, even if the provider does not think the vaccine caused that event” (Link).

 Let’s take a look at the math here (illustrated above). For a population of 100,000 the “all-cause death rate” is around 869.7 deaths per year (Link). For the first 3.5 months of since the COVID-19 vaccine campaign began, around 166 million people were vaccinated. Out of this population, 421,080 would be expected to die of natural causes within 3.5 months (~106 days). That gives us an average expected “all-cause” death rate of ~4000 people per day. Yet only a few hundred of these deaths are reported to VAERS on a given day? – as per the chart above? That’s the amazing thing… that so few of the deaths that must have happened the very same day as the vaccination was given are actually reported to VAERS!
Let’s take a look at the math here (illustrated above). For a population of 100,000 the “all-cause death rate” is around 869.7 deaths per year (Link). For the first 3.5 months of since the COVID-19 vaccine campaign began, around 166 million people were vaccinated. Out of this population, 421,080 would be expected to die of natural causes within 3.5 months (~106 days). That gives us an average expected “all-cause” death rate of ~4000 people per day. Yet only a few hundred of these deaths are reported to VAERS on a given day? – as per the chart above? That’s the amazing thing… that so few of the deaths that must have happened the very same day as the vaccination was given are actually reported to VAERS!

Myocarditis in Young Men Following 2nd mRNA Vaccine Dose:
Dr. McCullough noted that he sees patients who developed myocarditis (an inflammation of the heart) following vaccination for COVID-19, including one particularly serious case that doesn’t seem to be resolving and will probably end up with at least long-term damage to the heart, if not death, for a young male athlete. And, this is indeed a real, but rare, risk associated with the mRNA vaccines:
Myocarditis has been recognized as a rare complication of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) mRNA vaccinations, especially in young adult and adolescent males. According to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, myocarditis/pericarditis rates are ≈12.6 cases per million doses of second-dose mRNA vaccine among individuals 12 to 39 years of age… Although the mechanisms for development of myocarditis are not clear, molecular mimicry between the spike protein of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) and self-antigens, trigger of preexisting dysregulated immune pathways in certain individuals, immune response to mRNA, and activation of immunologic pathways, and dysregulated cytokine expression have been proposed. (Bozkurt, et. al., July 20, 2021).
Now, what McCullough fails to mention is that the risk of myocarditis is much higher for those who become infected by COVID-19. Even in young athletes, the rate of myocarditis following COVID-19 infection ranges from around 0.6% to 0.7% (Front. Cardiovasc. Med., 14 July 2021). That’s 6000 to 7000 young healthy athletes, per million, who come down with myocarditis following a COVID-19 infection – compared with ~12 per million following mRNA vaccination (up to 67 cases per million according to the CDC; Link).
So, either way you slice it, the odds of a young healthy person coming down with myocarditis are much greater following an infection by COVID-19 compared to the risk of myocarditis following full mRNA vaccination (by at least a ratio of 100:1). And, if one actually gets myocarditis, the risks of myocarditis are pretty much the same either way.
Myocarditis can cause sudden cardiac arrest and has been linked with 10%-20% of all sudden deaths in young athletes. COVID-19 myocarditis has been linked to several sudden cardiac deaths in patients who only had mild viral infection symptoms. (Link)
And, the same thing is true for every other risk there might be. For every risk associated with the mRNA vaccines, the very same risk is far higher for those who get infected by the COVID-19 virus.
As far as Pfizer being safer than Moderna, the difference, while real, is still very rare. The reason for the increased risk of Moderna, for myocarditis in young men, in particular (Link) is because the dose of Moderna is 100 μg while the dose for Pfizer is 30 μg. This increases the rate of myocarditis by 2.5x for Moderna as compared to Pfizer. Still, the myocarditis risk is far higher for those infected by COVID-19. This is true for almost every other risk you can name. The only reason one might think otherwise is if they only read and believe the misinformation and outright lies coming from conspiracy theory websites…
The Nuremberg Code and Informed Consent:
 But what about the Nuremberg Code? Dr. McCullough suggests that doctors and other medical providers are violating the Nuremberg Code (as well as the Declaration of Helsinki) when they give people vaccines against COVID-19 – since they are not being given adequate “informed consent” before being given the vaccine. Is this really the case?
But what about the Nuremberg Code? Dr. McCullough suggests that doctors and other medical providers are violating the Nuremberg Code (as well as the Declaration of Helsinki) when they give people vaccines against COVID-19 – since they are not being given adequate “informed consent” before being given the vaccine. Is this really the case?
The concept of informed consent in medical research grew largely out of unethical research projects conducted in the early 20th century, including the experiments during the Holocaust and the syphilis study done on black men without their consent in Tuskegee, Alabama, according to a paper from the Presidential Commission for the Study of Bioethical Issues, which distinguishes between the idea of informed consent for medical research and regular treatment.
The concept of informed consent in the health care setting, however, “developed from the intentional tort of battery, which protects individuals from an unwanted physical touching of the body by others having neither express nor implied consent of the person touched,” according to a paper published in the Mayo Clinic’s peer-reviewed journal. For more information on the history of all this see: Link
“Vaccines Don’t Work”:
 Every week the CDC puts out a “The Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report” or the MMWR (Link). According to Dr. McCullough, the MMWR report for July 30, 2021, up to two-thirds of those who are “fully vaccinated” are getting infected, exclaiming “Wait a minute! We have a problem!” He goes on to suggest that vaccines are creating a “superbug” – currently in the form of the Delta Variant of COVID-19.
Every week the CDC puts out a “The Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report” or the MMWR (Link). According to Dr. McCullough, the MMWR report for July 30, 2021, up to two-thirds of those who are “fully vaccinated” are getting infected, exclaiming “Wait a minute! We have a problem!” He goes on to suggest that vaccines are creating a “superbug” – currently in the form of the Delta Variant of COVID-19.Difference Between Infections and Hospitalizations/Deaths:
According to a report from Israel’s Health Ministry (July 20, 2021), Pfizer’s general effectiveness at preventing infections decreased as the time before exposure increased: efficacy was 79% for those who received their second dose in April, 69% for March, 44% for February, and 16% for people who were fully-vaccinated back in January – with an overall average of 42%.
This is interesting since it appears to conflict, somewhat, with the findings of another recent study (Jamie Bernal, et. al., May 24, 2021) which showed the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine to be 88% effective against symptomatic disease from the Delta Variant 2 weeks after the second dose, compared to 93% effectiveness against the Alpha Variant. Also, just one dose was found to be 33% effective against symptomatic disease from the Delta Variant after 3 weeks and 50% effective against the Alpha Variant.
On the other hand, the Mayo Clinic data is similar to data from Israel – which had one of the fastest vaccination programs in the world. According to data published in late July, the Pfizer vaccine was just 40.5% effective at preventing symptomatic disease.
Still, when it comes to the Delta Variant (>99% of cases in the US currently) the risk of hospitalization and death, and even infection, is much higher for those who are not vaccinated vs. those who are vaccinated (Scobie, et al., September 10, 2021):


Interferon Production and the Enhanced Childhood Resistance to COVID-19:
As a relevant aside, why is it, exactly, that children are so much more resistant to the COVID-19 virus? It’s all based on the enhancement of interferon in children as compared to adults (Loske, et. al., August 18, 2021). However, adults can also increase the rate of interferon production via the use of “fever production”. For additional information on how to effectively do this see Dr. Roger Seheult’s very interesting discussion of this topic:
The Kaiser Permanente Cohort Study:
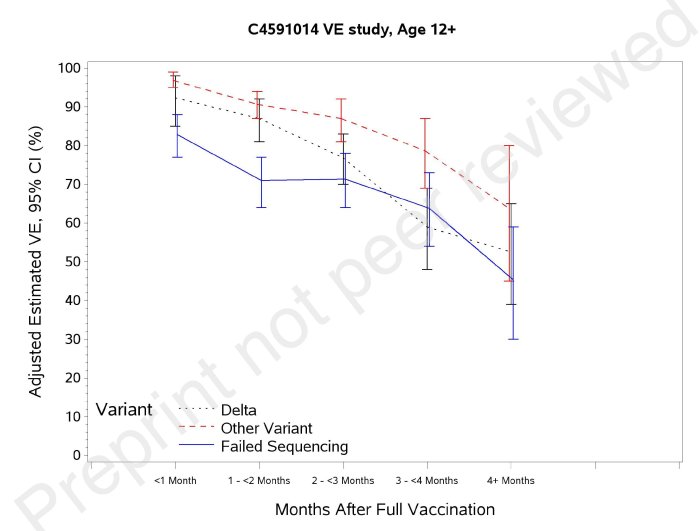
In this line, consider a 6-month follow-up of the Pfizer vaccination in a Kaiser Permanente cohort of >3.3 million people regarding the attrition of the effectiveness of the Pfizer vaccine, over a span of four months, when it came to preventing infections by the Delta Variant (Tartof et. al., August 23, 2021). Particularly note, however, that during this same period of time that the vaccine maintained strong protection against hospitalizations (93%).
 For additional helpful information along these lines, please also review the Twitter Feed of Dr. Eric Topol: Link
For additional helpful information along these lines, please also review the Twitter Feed of Dr. Eric Topol: Link
Dr. Topol is an American cardiologist, scientist, and author. He is the founder and director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute, a professor of Molecular Medicine at The Scripps Research Institute, and a senior consultant at the Division of Cardiovascular Diseases at Scripps Clinic in La Jolla, California. He is editor-in-chief of Medscape and theheart.org.
Differences between Pfizer and Moderna Vaccines against Delta Variant:
In any case, the Delta Variant of COVID-19 is far more infectious and transmissible compared to the original or “wild type” COVID-19 virus (Link). Early in the infection, when people are most likely to be contagious, the Delta variant seems to replicate in amounts that are perhaps 1,000 times as much as those seen in people infected with other variants, defeating immune defenses in the nose and throat for many people. It is 50% more contagious than the Alpha Variant, which was, in turn, around 50% more contagious than the original COVID-19 strain, with an incubation period of four days rather than six days – meaning people are contagious earlier. Preliminary studies also suggest that it may lead to more severe disease in the unvaccinated population. Additionally, the Delta Variant is resistant to some antibody treatments previously used to help very sick patients. Perhaps this is why a recent study from the United Kingdom showed that children and adults under 50 were 2.5 times more likely to become infected with the Delta Variant. And, since the mRNA vaccines were created to target the original COVID-19 virus, it is no surprise, then, that mutational variants will come along that are more resistant to the immunity produced by the mRNA vaccines.
But what is the reason for the difference in immunity, against the Delta Variant, between the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines? Why does the Moderna vaccine appear to have superior activity against the Delta Variant as compared to the Pfizer vaccine? Well, consider that each dose of Pfizer’s contains 30 μg of vaccine while each dose of Moderna contains 100 μg of vaccine – which translates into more than 3x the number of mRNA molecules injected for Moderna as compared to Pfizer. This is the primary difference between these two vaccines. Otherwise, the mRNA sequence, itself, is identical for both vaccines.
As far as Pfizer being safer than Moderna, the difference, while real, is still very rare. The reason for the increased risk of Moderna, for myocarditis in young men, in particular (Link) is because the dose of Moderna is 100 μg while the dose for Pfizer is 30 μg. This increases the rate of myocarditis by 2.5x for Moderna as compared to Pfizer. Still, the myocarditis risk is far higher for those infected by COVID-19. This is true for almost every other risk you can name. The only reason one might think otherwise is if they only read and believe the misinformation and outright lies coming from conspiracy theory websites…
Number of Spike Proteins via Vaccines vs. Infection:
 As an interesting aside, on average, a single mRNA is used to manufacture about 900 copies of the corresponding protein within a given cell (Link). Now, one Moderna vaccine dose contains about 4 ×1013 mRNA molecules (~40 trillion) while one dose of the Pfizer vaccine contains about 1.2 ×1012 mRNA molecules (~12 trillion). If each one of these molecules produces, say, 1000 spike proteins, that can end up producing up to ~1 ×1016 spike proteins (Link).
As an interesting aside, on average, a single mRNA is used to manufacture about 900 copies of the corresponding protein within a given cell (Link). Now, one Moderna vaccine dose contains about 4 ×1013 mRNA molecules (~40 trillion) while one dose of the Pfizer vaccine contains about 1.2 ×1012 mRNA molecules (~12 trillion). If each one of these molecules produces, say, 1000 spike proteins, that can end up producing up to ~1 ×1016 spike proteins (Link).
Now, in comparison, an infected person carries 109–1011 virions during peak infection with a total of up to 3×1012 virions over the complete course of a characteristic infection (Link). Each of these viruses has around 24 spike proteins on its surface (Link), for a total of ~1×1014 spike proteins.
So, isn’t this a problem? given that the mRNA vaccines end up producing around 100x more spike proteins within the human body as compared to an actual COVID-19 infection? Well, remember that more than 99% of the spike proteins produced by the mRNA vaccines remain at the injection site. Less than 1% makes it to the bloodstream, and most of these spike proteins are filtered out by the liver (Link). In comparison, an infection by COVID-19 spreads throughout the body with active viral replication destroying tissues and targeting the cells that line blood vessels, producing blood clots everywhere. These blood clots end up damaging various organs, including the lungs, kidneys, heart, and brain.
mRNA vaccines more effective than no vaccines against infection:
 So, while the effectiveness of the mRNA vaccines against being infected by COVID-19 has dropped, it hasn’t dropped to zero. In other words, getting the Pfizer vaccine, for example, is still 42% more effective at blocking an infection by the Delta Variant of COVID-19 as compared to those who haven’t been vaccinated at all (76% better for those fully vaccinate with Moderna vs. no vaccine).
So, while the effectiveness of the mRNA vaccines against being infected by COVID-19 has dropped, it hasn’t dropped to zero. In other words, getting the Pfizer vaccine, for example, is still 42% more effective at blocking an infection by the Delta Variant of COVID-19 as compared to those who haven’t been vaccinated at all (76% better for those fully vaccinate with Moderna vs. no vaccine).
mRNA vaccines still very effective against hospitalizations and death:

 What is also very important to remember here is how the mRNA vaccines affect the rate of serious sickness – i.e., hospitalizations and deaths. Those who are fully vaccinated are far far less likely to be hospitalized or die due to a COVID-19 infection as compared to those who are not vaccinated.
What is also very important to remember here is how the mRNA vaccines affect the rate of serious sickness – i.e., hospitalizations and deaths. Those who are fully vaccinated are far far less likely to be hospitalized or die due to a COVID-19 infection as compared to those who are not vaccinated.
Before the Delta Variant came long, fully vaccinated people accounted for less than 3% of coronavirus hospitalizations nationwide and less than 1% of virus deaths. By the end of July, the Delta Variant was the cause of more than 80% of new U.S. COVID-19 cases. So, how has this affected the hospitalization/death rates of the fully vaccinated compared to the unvaccinated?
The authors of the Mayo Clinic study themselves concluded that both the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines “strongly protect” against severe disease via the Delta Variant; “The difference appears to be more about whether people get infected at all in the first place.” (Link) Dr. Shira Doron of Tufts Medical Center noted that the mRNA vaccines, while showing reduced effectiveness against infection, retained effectiveness against hospitalization of “over 95%” (Link). This is in line with another pre-print paper showing that the Pfizer vaccine is 96% effective against hospitalization after 2 doses (Julia Stowe, et. al., June 2021). This is comparable with vaccine effectiveness against hospitalization from the Alpha Variant.
Dr. Mary Ramsay, Head of Immunisation at PHE, noted that, “These hugely important findings confirm that the vaccines offer significant protection against hospitalization from the Delta variant.” (Link)
Dr. Gregory Poland, an infectious diseases physician and researcher at the Mayo Clinic, points out that the vaccines against COVID-19 are “extraordinarily effective against death, hospitalization, and severe disease.”

19% Death Rate for the Vaccinated:
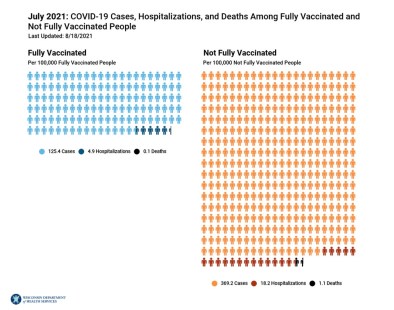 Again, as noted above, Dr. McCullough’s claim that the death rate for the vaccinated is around 19%, therefore they don’t prevent deaths, is nonsense. Somehow, Dr. McCullough fails to grasp the concept that in regions with very high vaccination rates that the most deaths will be in the vaccinated group – despite being highly protective. But how can that be?
Again, as noted above, Dr. McCullough’s claim that the death rate for the vaccinated is around 19%, therefore they don’t prevent deaths, is nonsense. Somehow, Dr. McCullough fails to grasp the concept that in regions with very high vaccination rates that the most deaths will be in the vaccinated group – despite being highly protective. But how can that be?
Consider a situation where 100% of a group of people were vaccinated with a vaccine that gives 95% protection. Over time, 5 people die. What percentage of these people were vaccinated? 100% – right? Is the conclusion, then, that because all of the dead people were vaccinated that the vaccine didn’t work? No. It just means that the vaccine wasn’t 100% effective.

The same thing is true, in a given age category, where more than 90% of people are vaccinated (as is true in Israel for those over the age of 60), but have between 12x and 82x the risk of serious infection as compared to someone in their 30s. Even if the vaccine’s effectiveness in preventing severe sickness and death were >90%, you’d still expect that a high relative percentage of the vaccinated would die in such a situation – at least 19% if not higher (see table below).

Jeffrey Morris, Director of the Biostatistics Division at the University of Pennsylvania (August 17, 2021)

 What matters for gauging vaccine effectiveness is not the proportion of hospitalized people who were vaccinated but the proportion of vaccinated people who wind up in the hospital. In fact, a high share of vaccinated people among the very sick could just be a sign that a lot of people have been vaccinated. Let’s say that vaccines are 95% effective, reducing someone’s chance of being hospitalized from 1% to 0.05%. And imagine that in a group of 1 million people, 90% were vaccinated. We’d expect 0.05% of the 900,000 vaccinated people — that is, 450 people — to go to the hospital. By comparison, we’d have 1% of the 100,000 unvaccinated people — 1,000 people — in the hospital. The vaccinated would account for about one out of every three hospitalizations (Link). So, when analyzing data like this, one must adjust for the overall vaccination rates within a particular age category and then go from there.
What matters for gauging vaccine effectiveness is not the proportion of hospitalized people who were vaccinated but the proportion of vaccinated people who wind up in the hospital. In fact, a high share of vaccinated people among the very sick could just be a sign that a lot of people have been vaccinated. Let’s say that vaccines are 95% effective, reducing someone’s chance of being hospitalized from 1% to 0.05%. And imagine that in a group of 1 million people, 90% were vaccinated. We’d expect 0.05% of the 900,000 vaccinated people — that is, 450 people — to go to the hospital. By comparison, we’d have 1% of the 100,000 unvaccinated people — 1,000 people — in the hospital. The vaccinated would account for about one out of every three hospitalizations (Link). So, when analyzing data like this, one must adjust for the overall vaccination rates within a particular age category and then go from there.
The Latest Data from Israel:
As far as the data coming from Israel is concerned, in particular, it seems that despite a recent increase in the number of serious cases, including among the fully vaccinated, those who received both doses of the vaccine against COVID-19 are significantly less likely to experience severe illness, according to data released by the Israeli Health Ministry.
As of August 16, the ministry recorded 159 severe COVID-19 cases per 100,000 people among the unvaccinated over the age of 60, compared to 20 per 100,000 people among the fully vaccinated. This makes the unvaccinated elderly more than eight times as likely to experience a severe case than their immunized counterparts.
For those under the age of 60, the rate of severe illness among the unvaccinated stood at 2.4 cases per 100,000 people – 2.7 times more than the 0.9 per 100,000 among those who are fully vaccinated.
According to the data, while the risk of experiencing severe symptoms increases with age for both the vaccinated and unvaccinated, it rises much more dramatically among the unvaccinated.
Speaking with Haaretz during a live Q&A last week, Prof. Ran Balicer, chairman of Israel’s expert panel on COVID-19, said “there’s no question” that people who are unvaccinated are at a higher risk of developing severe illness from COVID-19. While the effectiveness of the COVID-19 vaccine may have waned somewhat over the past several months, those who are vaccinated are protected five to 10 times as much as those who are unable or unwilling to receive the shot, said Prof. Nadav Davidovitch, director of the School of Public Health at Ben-Gurion University of the Desert, Be’er Sheva, and head of the Israeli Association of Public Health Physicians. (Sokol, August 16, 2021)
Significantly Increasing Case-Fatality Rate with Age:
Note also that the COVID-19 fatality rate increases dramatically with age – in Israel an in the US and everywhere throughout the world. Those under the age of 40 are relatively unlikely to die due to a symptomatic infection (0.1% case fatality rate). However, those in their 70s have a mortality risk that is 30x that for someone in their 30s. Of course, more young people are getting very sick and are dying with the Delta Variant since this past July. Dr. Roger Seheult just saw two people in their 30s die from COVID this past weekend (August 27-19, 2021). One of these was the son of an Adventist physician. All in his ICU this weekend were unvaccinated.
This also doesn’t take into account the much higher rate of long-term injuries for those who don’t die. Even young people have a fairly high rate of long-term injuries following a COVID-19 infection. The University of Washington researchers reported in February that about 33% of COVID-19 patients who were never sick enough to require hospitalization continue to complain months later of symptoms like fatigue, loss of smell or taste, and “brain fog.” Overall, almost 2 million COVID-19 patients (23.2%) sought treatment for COVID-related symptoms a month or more after being diagnosed. (Link)
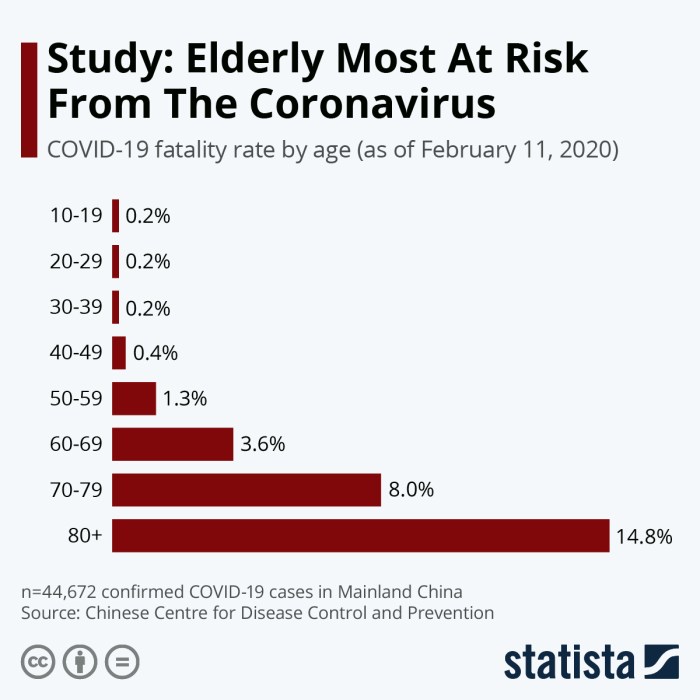
COVID-19 in Pregnancy:
Pregnant women with Covid-19 are 15 times more likely to die, 14 times more likely to need to be intubated, and 22 times more likely to have pre-term birth than those who are uninfected, according to a study published this month in JAMA Network Open. “I have not seen risks like this,” said Linda Eckert, professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Washington. (Stein, August 23, 2021)
Vaccines Creating a “SuperBug”:
If the vaccines against COVID-19 were creating “SuperBugs”, as Dr. McCullough claims, then one might think it fairly obvious that these bugs must have come from regions of the world where the vaccine concentrations are the highest. Yet, that’s not the case. The Delta Variant, for example, originated in India where only about 4% of people are fully vaccinated. The Lambda variant, or C.37, was first identified in Peru as early as August 2020 – which has a 22% full vaccination rate. So far, nothing of the kind has originated in highly vaccinated regions such as Israel, the UK, the US, Iceland, etc. So far, then, this doesn’t seem to support McCullough’s vaccine-produced SuperBug Theory much.
Vaccines are “Spreading the Virus”:
Not only does McCullough claim that vaccines are responsible for producing “SuperBugs”, but he also claims that vaccines are responsible for “spreading the virus” – claiming that those who are vaccinated have 250x the viral load, of the Delta Variant, compared to those who are not vaccinated [1:16:20 in the video].
Now, that’s a rather shocking claim. By what mechanism would those who are vaccinated be able to produce 250x the viral load as compared to those who are not vaccinated? Sure, as previously noted, early in the infection, when people are most likely to be contagious, the Delta Variant seems to replicate in amounts that are perhaps 1,000 times as much as those seen in people infected with other variants, defeating immune defenses in the nose and throat for many people. However, this increase in viral load isn’t just present in those who are vaccinated, but in the unvaccinated as well. And, this is exactly what studies have shown (Riemersma, et. al., July 31, 2021). In fact, studies have also shown that those who are unvaccinated carry a higher viral load compared to those who are vaccinated.
The SARS-CoV-2 culture of nasopharyngeal swabs was positive in 68.6% of vaccinated HCWs versus 84.9% of unvaccinated HCWs with primary infections (p = 0.005, t-test). As the probability of culture positivity depends on viral load19, this was corrected for using a probit regression model with both viral load and vaccination status as predictors. Figure 1C shows the probability of a positive culture for a given viral load in vaccinated and unvaccinated HCWs. A positive vaccination status significantly decreased the probability of culture positivity (p = 0.002, Wald test).
Does this, then, mean that vaccinated people can transmit the Delta Variant to other people? Yes, but less often and for a lesser amount of time compared to those who are unvaccinated since the vaccine still reduces the number of infections as well as the amount of time that an infected person is infectious.
This is backed up by another recent paper that showed not only do vaccines still offer fairly good protection from getting sick with Delta, but also help an infected person clear the viral load much faster.
Serial Ct values of individuals were analyzed as a surrogate marker for the viral load. The initial median initial Ct value did not differ between unvaccinated and fully vaccinated patients (unvaccinated median Ct 18.8 (14.9-22.7), vaccinated 19.2 (15.2-22.2), p=0.929). However, fully vaccinated patients had a faster rate of increase in Ct value over time compared with unvaccinated individuals, suggesting faster viral load decline:
And, additional support is provided by yet another paper published by Martinez et al., (September 2, 2021), which showed a much lower risk of viral transmission for vaccinated people as compared to unvaccinated people (Link). The data is based on pre-Delta variants, but is still interesting given the overall context of the above-described information that is based on the Delta Variant:
Five out of six fully vaccinated individuals remained viral culture-negative throughout their enrollment period, suggesting minimal shedding of infectious virus and little to no transmission risk. They also had either undetectable or sporadic viral genome loads in the nasal swabs. These data suggest that in 2 of the 4 fully vaccinated individuals for which both saliva and nasal swabs were collected, infection was initially established within the oral cavity or other saliva-exposed tissue site and was restricted from disseminating to the nasal passages. The total number of days that vaccinated individuals tested viral culture positive was significantly fewer than both newly vaccinated and unvaccinated groups, indicating that vaccination significantly reduces infectious virus shedding.
(Martinez et al., September 2, 2021)
But what about the paper cited by Dr. McCullough (Niesen et al., July 5, 2021) which showed a fairly significant decrease in genetic diversity with increasing vaccine use? Doesn’t this pose a problem when it comes to producing more and more resistant strains of the virus? Well, Dr. McCullough failed to mention that the authors of this paper disagree with his interpretation of their work since they themselves viewed vaccinations against COVID-19 as a limiting factor in the evolution of SARS-CoV-2:
This study presents the first known evidence that COVID19 vaccines are fundamentally restricting the evolutionary and antigenic escape pathways accessible to SARS-CoV-2. The societal benefit of mass vaccination may consequently go far beyond the widely reported mitigation of SARS-CoV-2 infection risk and amelioration of community transmission, to include stemming of rampant viral evolution.
Now, it’s fine to disagree with the authors of a particular paper and have very good reasons for doing so, but it might still be good to at least mention that the authors don’t actually agree with or support your conclusions regarding their work.
As far as my own personal opinion is concerned, it seems reasonable to me to see the antigen variability of the spike protein as relatively limited without a significant loss of function (the Delta Variant has 7 mutations compared to the original wild-type variant while the Delta-plus Variant, or AY.1, has 8 mutations). If the vaccinations force the virus into a corner, so to speak, where there is little room within protein sequence space left to maneuver, then that would be a good thing as far as subsequent vaccines and/or natural immunity to simply eliminate these last small regions of relative safety for the virus.
Limited Mutational Landscape:

On a more hopeful note, recent research studies suggest that the mutational “landscape”, or the various possible ways that the virus spike protein might mutate in a way that allows it to “escape” the immunity generated in response to the vaccines so far produced against COVID-19, is very “limited”. Why might this be? Well, because, if the spike protein mutates too much, it will lose its ability to attach to the ACE2 receptor on human cells – and therefore suffer a “loss of function”. So, there are only so many mutational options available to the small functionally-relevant sites of the spike protein before it no longer serves a “beneficial function” from the perspective of a virus that “wants” to cause as many infections as possible. And, that’s good news when it comes to the vaccines against COVID-19 and their ability to continue to effectively teach the human immune system how to keep fighting off the COVID-19 virus.
“The modest ensemble of mutations relative to the WT [wild type of COVID-19] shown to reduce vaccine efficacy might constitute the majority of all possible escape mutations.” (Rochman, et al., August 31, 2021)
This conclusion was also predicted by Roberto Burioni and Eric J. Topol in a letter published by the journal Nature Medicine (June 21, 2021).
Despite vigorous replication of the virus in these highly vaccinated communities, the world is yet to witness the emergence of variants able to ‘break through’ the vaccine-induced immunity. We cannot, of course, exclude the possibility of their emergence even in the near future, but molecular data gathered thus far have made it clear that the ‘evolutionary space’ that SARS-CoV-2 has for evading vaccine-induced immunity is remarkably narrow relative to that available for increases in transmission rates.
Therefore, while the world needs to remain on full alert in order to promptly detect the emergence of ‘vaccine-piercing’ variants and, in that case, rapidly update the available vaccines, there is reason for very cautious optimism.
Roberto Burioni and Eric J. Topol, Nature Medicine, June 21, 2021
Not a Single Failure of Natural Immunity:
But what about Dr. McCullough’s claim that while high levels of break-through infections, along with hospitalizations and deaths have been seen among the vaccinated, that there hasn’t been “A single failure of natural immunity”? Not a single failure? – really? Sure, natural immunity might have offered fairly equivalent protection, compared to the fully vaccinated, before the Delta Variant came along. A study put out by the Cleveland Clinic showed that those who previously tested positive for a SARS-CoV-2 infection did not get additional benefits from the vaccine (Shrestha, et. al., June 5, 2021). Amazingly, a COVID-19 infection did not occur in anyone over the five months of the study among 2579 individuals previously infected with COVID-19, including 1359 who did not take the vaccine. That’s truly amazing! – not a single case! Wow! Of course, Dr. McCullough failed to mention the study from Qatar that showed a very similar rate of COVID-19 infection in the vaccinated as compared to those with natural immunity (Bertollini, et. al., June 9, 2021).
The relative risk for PCR positivity was 0.22 (95% CI, 0.17-0.28) for vaccinated individuals and 0.26 (95% CI, 0.21-0.34) for individuals with prior infection compared with no record of vaccination or prior infection [emphasis added] – Bertollini, et. al., June 9, 2021
Regardless, this was still very very good news at the time! It was because of this that “herd immunity” was indeed looking very promising there for a while. I personally thought that herd immunity might be reached this fall because of this particular finding. Then, the Delta Variant came along and ruined it all.
Immunity after a previous infection “is highly variable from one person to the next — it may be barely present and not last for long for some persons,” said Dr. Richard A. Martinello, a Yale Medicine infectious diseases specialist and associate professor at Yale School of Medicine.
Perhaps this is why the Cleveland Clinic currently recommends getting vaccinated, even for those who have natural immunity from a prior infection and despite their own research, published in June before the Delta variant came along (Link).
This analysis demonstrated that natural immunity affords longer lasting and stronger protection against infection, symptomatic disease and hospitalization due to the Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2, compared to the BNT162b2 two-dose vaccine-induced immunity. Notably, individuals who were previously infected with SARS-CoV-2 and given a single dose of the BNT162b2 vaccine gained additional protection against the Delta variant. (Gazit, et. al., August 25, 2021)
.Sivan Gazit is a physician and researcher, deputy managing director of KSM Research and Innovation Center at Maccabi Healthcare Services..
The natural immune protection that develops after a SARS-CoV-2 infection offers considerably more of a shield against the Delta variant of the pandemic coronavirus than two doses of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine, according to a large Israeli study that some scientists wish came with a “Don’t try this at home” label. The newly released data show people who once had a SARS-CoV-2 infection were much less likely than vaccinated people to get Delta, develop symptoms from it, or become hospitalized with serious COVID-19.
The study demonstrates the power of the human immune system, but infectious disease experts emphasized that this vaccine and others for COVID-19 nonetheless remain highly protective against severe disease and death. And they caution that intentional infection among unvaccinated people would be extremely risky. “What we don’t want people to say is: ‘All right, I should go out and get infected, I should have an infection party.'” says Michel Nussenzweig, an immunologist at Rockefeller University who researches the immune response to SARS-CoV-2 and was not involved in the study. “Because somebody could die.”..
“These results suggest that boosting vaccinated individuals with currently available mRNA vaccines would produce a quantitative increase in plasma neutralizing activity but not the qualitative advantage against variants obtained by vaccinating convalescent individuals.”.
 And, there is also the problem of knowing if the COVID-19 infection one had was “good enough” to produce a high enough level of natural immunity – especially when it comes to the variants such as the Delta Variant. After all, a new study showed that the “percentage of variant cross-binding memory B cells was higher in vaccinees than individuals who recovered from mild COVID-19.” (Goel, et al., August 23, 2021) In this regard, it seems as though those who were vaccinated have an advantage in that the resulting immunity is more consistent and predictable as compared to natural immunity. These higher levels of memory B-cells within vaccinated people may also be the reason for the long-term protection against hospitalizations and deaths – despite the waining levels of antibody levels against the virus over time. Memory B-cells can be “awakened” when an infection hits the body, a pre-formed arm that is ready to fight off the repeat offender.
And, there is also the problem of knowing if the COVID-19 infection one had was “good enough” to produce a high enough level of natural immunity – especially when it comes to the variants such as the Delta Variant. After all, a new study showed that the “percentage of variant cross-binding memory B cells was higher in vaccinees than individuals who recovered from mild COVID-19.” (Goel, et al., August 23, 2021) In this regard, it seems as though those who were vaccinated have an advantage in that the resulting immunity is more consistent and predictable as compared to natural immunity. These higher levels of memory B-cells within vaccinated people may also be the reason for the long-term protection against hospitalizations and deaths – despite the waining levels of antibody levels against the virus over time. Memory B-cells can be “awakened” when an infection hits the body, a pre-formed arm that is ready to fight off the repeat offender.Delta Variant More or Less Deadly:
Of course, it is also interesting to note that the current CFR (case fatality rate) in the US for the last 30 days, prior to September 6, 2021 (largely due to the delta variant) is 0.6%. Does this mean that the delta variant is, therefore, less lethal? Not necessarily since the current CFR may be reduced due to the vaccination rate and the rate of natural immunity that is much higher now as compared to the situation before 2021. Still, it is interesting to note that in June (2021), just before the delta variant became prominent in the US, the CFR was much higher at 2.6%. In May it was also higher at 1.92%. And, this higher fatality rate has remained remarkably consistent since widespread vaccinations were made available in early 2021. Then, suddenly, in July, when the Delta Variant became dominant, the CFR dropped significantly. Why would this happen so suddenly unless the delta variant were, in fact, significantly less deadly? Since hospitalizations have indeed risen in recent weeks, it is entirely possible that the death rate will rise dramatically in August, but that just hasn’t happened as in the past.
 What’s the most likely reason for this? Could it be that the Delta Variant is simply less deadly compared to previous variants? Perhaps. Or, perhaps it’s just because the Delta Variant is affecting a younger population in a context of higher vaccination rates and natural immunity? That’s also possible. Dr. Amesh Adalja, a senior scholar at the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security, said: “All variants are going to have a lower case fatality rate, because a significant portion of the population, especially those at high risk for death, are fully or partially vaccinated.” (Link)
What’s the most likely reason for this? Could it be that the Delta Variant is simply less deadly compared to previous variants? Perhaps. Or, perhaps it’s just because the Delta Variant is affecting a younger population in a context of higher vaccination rates and natural immunity? That’s also possible. Dr. Amesh Adalja, a senior scholar at the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security, said: “All variants are going to have a lower case fatality rate, because a significant portion of the population, especially those at high risk for death, are fully or partially vaccinated.” (Link)
In any case, it does seem that children are getting hit pretty hard by the Delta Variant. The hospitalization and ICU admission rates are rapidly approaching the highest pre-Delta levels (Siegel et al., September 3, 2021). Emergency department visits and hospital admissions in a 2-week period in August 2021 were higher in the 0-17 age group in states with lower population vaccination coverage and lower in states with higher vaccination coverage (Link).


Hard to Transmit the COVID-19 Virus:
 Dr. McCullough made a very interesting claim at one point in his presentation. He said that the COVID-19 virus is relatively hard to transmit between people, so much so that it is pretty much impossible to get infected if one is outside. And, if inside, that it takes a long time of exposure, around “three hours” of being in close proximity, for an infection to take place.
Dr. McCullough made a very interesting claim at one point in his presentation. He said that the COVID-19 virus is relatively hard to transmit between people, so much so that it is pretty much impossible to get infected if one is outside. And, if inside, that it takes a long time of exposure, around “three hours” of being in close proximity, for an infection to take place.Delta Variant far more Infectious:
The basic reproduction number (R0) of SARS-CoV-2 has been estimated to be as high as 5.7, meaning that one infected person can be expected to spread the infection to 5.7 others, on average, in a population of susceptible individuals. This number is much higher than typically seen with more common respiratory tract infections, including seasonal influenza (R0 = 1.3) and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) (R0 = 3.0). This means the virus is extremely contagious and has the potential to spread rapidly throughout communities, as has been demonstrated. (Haston and Pickering, May 21, 2021)
 There have also been a number of “superspreader events” where large gatherings, outside, ended up with many people being infected by the Delta Variant. For example, consider a series of large public events that occurred over several days in Cape Cod, Massachusetts (from July 3–17). This “event” or “series of events” if you prefer, resulted in 469 people being infected with Covid-19 (as initially reported by the CDC), with later estimates, Including people from other states, of 900 people being infected. (Link, Link)
There have also been a number of “superspreader events” where large gatherings, outside, ended up with many people being infected by the Delta Variant. For example, consider a series of large public events that occurred over several days in Cape Cod, Massachusetts (from July 3–17). This “event” or “series of events” if you prefer, resulted in 469 people being infected with Covid-19 (as initially reported by the CDC), with later estimates, Including people from other states, of 900 people being infected. (Link, Link)Presymptomatic Delta Transmission Rate of 74%:
An earlier study and an unpublished analysis by Cowling and others estimate that before Delta emerged, individuals infected with SARS-CoV-2 took an average of 6.3 days to develop symptoms and 5.5 days to test positive for viral RNA, leaving a narrower window of 0.8 days for oblivious viral shedding.
In the latest work, the researchers also found that those infected with Delta had higher concentrations of viral particles, or viral load, in their bodies than did people infected with the original version of SARS-CoV-2. “Somehow the virus is appearing quicker and in higher amounts,” says Cowling.
As a result, 74% of infections with Delta took place during the presymptomatic phase — a higher proportion than for previous variants. This high rate “helps explain how this variant has been able to outpace both the wild-type virus and other variants to become the dominant strain worldwide”, says Barnaby Young, an infectious-disease clinician at the National Centre for Infectious Diseases in Singapore.
Masks Effective at Reducing Transmission:
The Vaccinated are Killing the Unvaccinated:
Amazingly, when McCullough, who was asked to comment on the 90-95% of covid patients in the hospital being those who are unvaccinated, claimed that they likely contracted it from the vaccinated. He was blaming the vaccinated for infecting and causing the hospitalizations of the unvaccinated (August 21 Panel Discussion). Now, while it is true that the Delta Variant has a higher rate of “break-through infections”, as discussed above, and while it is also true that this can result in an infected vaccinated person transmitting the virus to someone else, it is also true that an infected vaccinated person is less infectious and for a shorter amount of time compared to someone who is not vaccinated who gets infected (Chia, et al. July 31, 2021). Delta viral loads were similar for both groups for the first week of infection, but dropped quickly after day 7 in vaccinated people.
In this line, consider another recent preprint paper available on medRxiv:
Our data support that the SARS-CoV-2 infectious virus shedding is lower in vaccinated individuals with breakthrough infections (caused by primarily the delta variant) than in unvaccinated individuals with primary infections (caused by SARS-CoV-2 D614G). Nevertheless, virus culture was positive in 68.6% of breakthrough infections and Ct-values decreased throughout the first three days of illness. Despite the reduced viral viability, the infectivity of individuals with breakthrough infections should not be neglected. (Shamier, et. al., August 21, 2021)
Also, consider the results of the “REACT-1 Study” where the researchers found that “fully vaccinated people in this testing round had between around 50% to 60% reduced risk of infection [Delta Variant], including asymptomatic infection, compared to unvaccinated people. In addition, double vaccinated people were less likely than unvaccinated people to test positive after coming into contact with someone who had COVID-19 (3.84% vs 7.23%)” (Link). “Fully vaccinated people who were infected with the virus tended to have less severe illness than unvaccinated people and seemed to have smaller amounts of virus in samples, the researchers added, meaning they may be less likely to pass it on if they are infected” (Link).
Paul Elliott, an epidemiologist at Imperial, says that these results differ from other Ct studies because this REACT-1 study sampled the population at random and included people who tested positive without showing symptoms. (Link)
Risks of mRNA Vaccines vs. Risks of COVID-19:
COVID-19 Infections Much More Risky:
When it comes to analyzing the risks of vaccination vs. getting infected by COVID-19, it would be good to review a large important scientific study of Pfizer mRNA vaccination (>884,000 people and controls) vs Covid infection (>173,000 people and controls). This study provides clear evidence regarding the relative safety of the mRNA vaccines vs. the other option of getting infected by COVID-19 (Barda, et. al., August 25, 2021). With the exception of lymphadenopathy (a benign self-limited reactive condition), pretty much every other risk one can think of for the mRNA vaccines is far surpassed when it comes to getting infected by COVID-19. In fact, getting vaccinated was substantially protective against numerous key adverse events – such as “anemia, acute kidney injury, intracranial hemorrhage, and lymphopenia.”
In this study in a nationwide mass vaccination setting, the BNT162b2 [Pfizer] vaccine was not associated with an elevated risk of most of the adverse events examined. The main potential adverse events identified included an excess risk of lymphadenopathy (78.4 events per 100,000 persons), herpes zoster infection (15.8 events), appendicitis (5.0 events), Bell’s palsy(8 excess events per 100,000 persons), and myocarditis (2.7 events – 1 to 5 events per 100,000 persons). The risk of this potentially serious adverse event [myocarditis] and of many other serious adverse events was substantially increased after SARS-CoV-2 infection. SARS-CoV-2 infection was estimated to substantially increase the risk of several adverse events for which vaccination was not found to increase the risk, including an estimated excess risk of arrhythmia (166.1 events per 100,000 persons), acute kidney injury (125.4 events), pulmonary embolism (61.7 events), deep-vein thrombosis (43.0 events), myocardial infarction (25.1 events), pericarditis (10.9 events), and intracranial hemorrhage (7.6 events).
We estimated that the BNT162b2 vaccine resulted in an increased incidence of a few adverse events over a 42-day follow-up period. Although most of these events were mild, some of them, such as myocarditis, could be potentially serious. However, our results indicate that SARS-CoV-2 infection is itself a very strong risk factor for myocarditis, and it also substantially increases the risk of multiple other serious adverse events.
The Claims of Contamination:
 I see blood smears from vaccinated people all the time. There are no abnormalities related to vaccination. I’ve also seen pictures and videos posted by anti-vaxx conspiracy theorists supposedly of the vaccine itself that show all kinds of “contaminants”. The problem here is that those who post such videos and pictures evidently don’t work much with microscopes since these “contaminants” are nothing more than the artifacts that are commonly seen when one uses a non-sterilized slide where artifacts of dust and micro-fibers and even bubbles are common. Also, the wild claim that the vaccines are made with graphene oxide and that graphene oxide is a “toxin” isn’t true. There is no “graphene oxide” in the vaccines against COVID-19 (Link, Link). Also, graphene oxide, which can be produced by writing with a pencil on a piece of paper, isn’t toxic to humans unless used in high quantities. Those like Dr. Carrie Madej who post such videos and pictures of vaccine “contaminants” simply don’t spend much time looking in microscopes. Dr. Madej also has a history of making wild conspiratorial claims against the vaccines against COVID-19. For example, she claimed that these vaccines will “hook us all up to an artificial intelligence interface” and will “change a person’s DNA” so that a vaccinated person “can be patented and owned” – of course, all masterminded by Bill Gates. This is all nonsense.
I see blood smears from vaccinated people all the time. There are no abnormalities related to vaccination. I’ve also seen pictures and videos posted by anti-vaxx conspiracy theorists supposedly of the vaccine itself that show all kinds of “contaminants”. The problem here is that those who post such videos and pictures evidently don’t work much with microscopes since these “contaminants” are nothing more than the artifacts that are commonly seen when one uses a non-sterilized slide where artifacts of dust and micro-fibers and even bubbles are common. Also, the wild claim that the vaccines are made with graphene oxide and that graphene oxide is a “toxin” isn’t true. There is no “graphene oxide” in the vaccines against COVID-19 (Link, Link). Also, graphene oxide, which can be produced by writing with a pencil on a piece of paper, isn’t toxic to humans unless used in high quantities. Those like Dr. Carrie Madej who post such videos and pictures of vaccine “contaminants” simply don’t spend much time looking in microscopes. Dr. Madej also has a history of making wild conspiratorial claims against the vaccines against COVID-19. For example, she claimed that these vaccines will “hook us all up to an artificial intelligence interface” and will “change a person’s DNA” so that a vaccinated person “can be patented and owned” – of course, all masterminded by Bill Gates. This is all nonsense.As far as autopsies, I don’t personally do those much anymore, but I still see a lot of tissues, under the microscope, every day from those who have been vaccinated – and there just isn’t anything abnormal that would be related to the vaccines.
All-Cause Excess Deaths:
Consider also that there has been a significant increase in all-cause “excess deaths” in the US and around the world, starting in March of 2020, because of this pandemic – an excess that is very difficult to explain as being due to anything other than COVID-19. In fact, the actual number of deaths being officially attributed to COVID-19 (currently over 650,000 deaths in the US) seems to be an undercount of the actual number of deaths that are being directly or indirectly caused by COVID-19. (Link)
Early Treatment:
Most Relied upon Slide in the World:

.
The Good:
 Do steroids, aspirin, and blood-thinners help those with COVID-19 infections survive? Sure they do.
Do steroids, aspirin, and blood-thinners help those with COVID-19 infections survive? Sure they do.
What about monoclonal antibodies like Bamlanivimab, Casirivimab, or Imdevimab? Absolutely beneficial! In fact, Sotrovimab, the newest antibody therapy has even more remarkable breadth and efficacy. It was developed by GlaxoSmithKline and Vir Biotechnology after a large collaborative study by scientists from across the nation discovered a natural antibody – in the blood of a SARS survivor, back in 2003. Experiments have shown that this antibody, called S309, neutralizes all known SARS-CoV-2 strains – including newly emerged mutants that can now “escape” from previous antibody therapies – as well as the closely related original SARS-CoV virus.
What about maintaining a good vitamin D level before infection? or perhaps trying to improve one’s vitamin D level early on in infection? Sure, that has some reasonable data support as well (Link). What about vitamin C and zinc along with some Quercitin? I’m more neutral here, but it couldn’t hurt.
 For additional recommendations from Harvard Heath (September 7, 2021): Link
For additional recommendations from Harvard Heath (September 7, 2021): Link
The Bad:
Where I have problems with this “Multidrug Therapy Protocol” is with Dr. McCullough’s recommendation for drugs like hydroxychloroquine and ivermectin.
Hydroxychloroquine:
 Sure, like pretty much everyone else, I was intrigued by the possibilities of hydroxychloroquine when it was first suggested as a possible treatment option for those suffering with COVID-19 infections. After all, it is a “zinc ionophore” (it helps zinc enter the cells of the human body to produce the anti-viral effects associated with zinc). Therefore, before the vaccines came along, many thought that it might at least be worth a try and were quite hopeful that it would work (Link). Unfortunately, however, this hypothesis hasn’t been very well supported by real-world scientific studies into this question. As it turns out, “Zinc supplements did not enhance the clinical efficacy of HCQ.” (Abd-Elsalam, et. al., November 2020).
Sure, like pretty much everyone else, I was intrigued by the possibilities of hydroxychloroquine when it was first suggested as a possible treatment option for those suffering with COVID-19 infections. After all, it is a “zinc ionophore” (it helps zinc enter the cells of the human body to produce the anti-viral effects associated with zinc). Therefore, before the vaccines came along, many thought that it might at least be worth a try and were quite hopeful that it would work (Link). Unfortunately, however, this hypothesis hasn’t been very well supported by real-world scientific studies into this question. As it turns out, “Zinc supplements did not enhance the clinical efficacy of HCQ.” (Abd-Elsalam, et. al., November 2020).
Ivermectin:
 But what about ivermectin? the anti-parasite drug usually used to deworm farm animals? Well, those like Dr. McCullough and Dr. Kory (who strongly supported the use of ivermectin before the US Senate). And, as with hydroxychloroquine, ivermectin seemed to show some promising results during some in vitro studies (performed or taking place in a test tube, culture dish, or elsewhere outside a living organism). However, when it came to real life with real people, actual scientific studies weren’t so promising. I wish Dr. McCullough and Dr. Kory were right about ivermectin. However, unfortunately, it doesn’t seem as though they are. That appears to be the unfortunate truth of the situation. (Link, Link)
But what about ivermectin? the anti-parasite drug usually used to deworm farm animals? Well, those like Dr. McCullough and Dr. Kory (who strongly supported the use of ivermectin before the US Senate). And, as with hydroxychloroquine, ivermectin seemed to show some promising results during some in vitro studies (performed or taking place in a test tube, culture dish, or elsewhere outside a living organism). However, when it came to real life with real people, actual scientific studies weren’t so promising. I wish Dr. McCullough and Dr. Kory were right about ivermectin. However, unfortunately, it doesn’t seem as though they are. That appears to be the unfortunate truth of the situation. (Link, Link)
In fact, countries that initially relied heavily on ivermectin to prevent and treat COVID-19, like Brazil and India for example, have paid dearly for this mistake with the sacrifice of a great many lives. Ivermectin, as well as the once touted hydroxychloroquine, have now been removed from the treatment protocols for both Brazil and India due to a lack of useful benefits (Link, Link).
More Background History on Ivermectin vs. COVID-19:
 Now, a bit more history is interesting regarding ivermectin, in particular. I’ve had many people send me the very same meta-analysis published paper by Dr. Pierre Kory (Link) – along with the argument that ivermectin clearly works “if given early enough” following infection. The problem with these “meta-analysis” studies is that putting together an analysis on a bunch of small studies that individually have limited predictive power doesn’t necessarily make the overall meta-analysis any better than the largest and most statistically significant single underlying study. As Gorski and others point out, meta-analyses are only as good as their raw material – a phenomenon Gorski labels “garbage in, garbage out.” That’s the reason why larger double-blinded placebo-controlled trials are seen as more reliable, generally speaking, compared to meta-analysis papers. The problem here is that the preliminary results from such a trial, known as the “Together Trial” (consisting of nearly 2300 participants in a Phase 3 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial), showed no significant effect on reducing emergency room visits or hospitalizations – despite “early treatment”.
Now, a bit more history is interesting regarding ivermectin, in particular. I’ve had many people send me the very same meta-analysis published paper by Dr. Pierre Kory (Link) – along with the argument that ivermectin clearly works “if given early enough” following infection. The problem with these “meta-analysis” studies is that putting together an analysis on a bunch of small studies that individually have limited predictive power doesn’t necessarily make the overall meta-analysis any better than the largest and most statistically significant single underlying study. As Gorski and others point out, meta-analyses are only as good as their raw material – a phenomenon Gorski labels “garbage in, garbage out.” That’s the reason why larger double-blinded placebo-controlled trials are seen as more reliable, generally speaking, compared to meta-analysis papers. The problem here is that the preliminary results from such a trial, known as the “Together Trial” (consisting of nearly 2300 participants in a Phase 3 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial), showed no significant effect on reducing emergency room visits or hospitalizations – despite “early treatment”.
Another smaller double-blinded randomized placebo-controlled trial, involving 476 patients, also failed to show any advantage for ivermectin use (Lopez-Medina, March 4, 2021).
Now, some might suggest that the findings of these trials might be due to some sort of bias. Perhaps, but I don’t see how this is likely. This is especially true given that the particular meta-analysis paper published by Dr. Kory was published on April 22, 2021. Why might this be a problem? Because, it was published before the paper published by Dr. Ahmed Elgazzar (from Benha University in Egypt) was withdrawn because it was shown to be fraudulent (originally published on the Research Square website in November of 2020) (Link). Now, Dr. Kory’s meta-analysis paper depends heavily upon the Elgazzar paper – which is now known to be completely worthless. And, if one removes the Egypt data and re-runs the meta-analysis, “the benefit…largely loses its statistical significance.” (Link)
Now, I really wish there were clear evidence that ivermectin and/or hydroxychloroquine worked, but so far, I just don’t see the claims in this regard as being supported by the weight of evidence that is currently in hand.
Do I think Dr. Kory was lying? No. I think he really believed in and probably still believes in ivermectin as a useful treatment for COVID-19. I just think that various treatment protocols, that I think have shown some good success as described above, which are attributed to ivermectin and/or hydroxychloroquine as part of these protocols, are far more likely to be the result of some of the other drugs that are being used at the very same time – such as steroids, monoclonal antibodies, etc…
For a good summary article on ivermectin vs. COVID-19 see: Dr. Nick Mark, September 30, 2021
For a good paper dealing with reasons why the meta-analysis papers favoring ivermectin as a miraculous treatment for COVID-19 were so flawed see: Lawrence et al., September 22, 2021
McCullough before the Senate Homeland Security Committee:
 On November 19, 2020, Dr. McCullough testified, along with a number of other medical professionals, before a Senate Homeland Security Committee hearing – while holding up his “most relied upon slide in the world” (Link). He argued that the use of hydroxychloroquine earlier in the pandemic to treat outpatients with early symptoms helped to mitigate the severity of the outbreak.
On November 19, 2020, Dr. McCullough testified, along with a number of other medical professionals, before a Senate Homeland Security Committee hearing – while holding up his “most relied upon slide in the world” (Link). He argued that the use of hydroxychloroquine earlier in the pandemic to treat outpatients with early symptoms helped to mitigate the severity of the outbreak.
“Hydroxychloroquine was widely used early on, that’s what kept the March-April-May curve down, OK?”
 Dr. Harvey Risch, another of the expert witnesses from Yale University, said in his testimony that he found hydroxychloroquine in early use among high-risk outpatients to be “exceedingly safe”. He went on to testify that “studies of hydroxychloroquine early use in high-risk outpatients, every one of them, and there are now seven studies, have shown significant benefit.” (Link)
Dr. Harvey Risch, another of the expert witnesses from Yale University, said in his testimony that he found hydroxychloroquine in early use among high-risk outpatients to be “exceedingly safe”. He went on to testify that “studies of hydroxychloroquine early use in high-risk outpatients, every one of them, and there are now seven studies, have shown significant benefit.” (Link)
Of course, these studies were observational in nature. Dr. Ashish Jha, one of the others doctors who gave testimony, argued meant this meant that they were not of high quality – and thus the results should be treated with caution. He also pointed out that, “Hydroxychloroquine has a very narrow therapeutic range. Only a small range of doses can be tolerated without leading to toxicity. While hydroxychloroquine toxicity is not very common, its use for COVID-19 requires a higher dosage than normally employed, and therefore, raises concern of greater side-effects and toxicity.”
Overall, Dr. Jha was not pleased at all that the Senate was even having such a hearing:
The Senate Homeland Security and Governmental Affairs Committee held a hearing about early treatment for Covid-19. Yet instead of a robust discussion about promising emerging therapies or what Congress might do to accelerate such treatments, the conversation was all about the malaria drug hydroxychloroquine. That’s right. Almost nine months into the pandemic, during a surge, with 1,500 daily deaths, senators saw fit to rehash a medical dead end. Trial after trial has found no evidence that hydroxychloroquine improves outcomes for Covid-19 patients; some studies have found that it causes more harm than good…
In the hearing, I was called “reckless” because I pointed to facts that could prevent people from getting this treatment. The evidence itself, they seemed to be arguing, was the misinformation…
Senator Johnson and his witnesses questioned the integrity of the medical community, suggesting scientists were part of some “deep state” conspiracy to deny Americans access to lifesaving therapies…
By elevating witnesses who sound smart but endorse unfounded therapies, we risk jeopardizing a century’s work of medical progress. Do we really want to go back to valuing anecdote over data, and no longer use the best evidence to decide which treatments work?
And, it’s no different today. Dr. McCullough continues to promote his ideas, not via the support of careful scientific research, but via personal experience or gut feelings along with anecdotal stories which he fleshes out with appeals to weak observational studies and meta-analyses of these studies that simply haven’t been supported by the subsequent double-blinded placebo-controlled trials (on hydroxychloroquine or ivermectin).
Now, I’m all for the early treatment of those infected by COVID-19, but not with treatments where the weight of current scientific evidence simply isn’t there.
And… The Ugly:
Single Drugs Don’t Work:
So, how does Dr. McCullough respond to all the evidence that drugs like ivermectin and hydroxychloroquine don’t seem to work in real life? Well, he excuses all of these very good scientific studies by saying that you have to use “multiple drugs” as in HIV – that single drugs used by themselves “don’t work”. Of course, what Dr. McCullough neglects to mention is that in general multidrug cocktails against infections like HIV each contain drugs where each individual drug, within the cocktail of drugs being used, has at least some known benefit against the infection in question. You can’t just throw together drugs that don’t work at all by themselves and expect that they will suddenly work if used in combination – Dr. Vincent Iannelli explains (Link).
Of course, what Dr. McCullough claims to have done is to “leverage” small clinical trials and observational studies; too bad he didn’t do the RCTs of his cocktail, which, given the rapidly fatal course of severe COVID-19, would, contrary to his claim, not take “years” to get results from.
Finally, like all Brave Mavericks, Dr. McCullough claims that the reason his protocol isn’t widely accepted and publicized isn’t because it doesn’t work, but rather because the press and government regulatory agencies are either ignoring or “suppressing” news of it, even as he cited a “home treatment guide” published by—you guessed it!—AAPS. Basically, his protocol includes one FDA-accepted drug, Regeneron’s monoclonal antibody cocktail that was issued an EUA, followed by vitamins (of course!), steroids (another drug that works) and—also of course!—hydroxychloroquine, ivermectin, zinc, and azithromycin, none of which have been shown to work. Come to think of it, he’s very much like Stanislaw Burzynski, mixing the unproven with the weakly proven and claiming without evidence to have “saved thousands of lives” and claims he could have saved 50-85% of the lives lost to COVID-19. Again, there’s no solid evidence to support any of these claims. I will give him one point. He’s not entirely wrong that the US has decided to emphasize vaccination as the answer to the pandemic, but he also dismisses masking and social distancing as having been overemphasized.
Summary (5-minute read):
So, what are the most important takeaway points here? Well, for me, here’s what strikes me as the most important things to remember when it comes to the main points presented by Dr. McCullough vs. what seems to be the reality of the real-world evidence that is currently in hand:
VAERS Reporting:
The Claim:
 Dr. McCullough claims that the spike in reported cases to the VAERS database of reportable adverse reactions following vaccination (maintained by the CDC and the FDA) is strong evidence that the vaccines against COVID-19 have killed over 100,000 people and have seriously injured many many more.
Dr. McCullough claims that the spike in reported cases to the VAERS database of reportable adverse reactions following vaccination (maintained by the CDC and the FDA) is strong evidence that the vaccines against COVID-19 have killed over 100,000 people and have seriously injured many many more.
Reality:
 However, upon closer inspection, this data is best explained by enhanced reporting due to the very well-known and well-publicized, and even the politicized, nature of the pandemic that we’re in – throughout the entire world. This same kind of spike in VAERS reporting has occurred in the past during other well-publicized pandemics, so is only to be expected. Over time, as people have become more and more used to the vaccines, however, the reporting to VAERS has steadily decreased.
However, upon closer inspection, this data is best explained by enhanced reporting due to the very well-known and well-publicized, and even the politicized, nature of the pandemic that we’re in – throughout the entire world. This same kind of spike in VAERS reporting has occurred in the past during other well-publicized pandemics, so is only to be expected. Over time, as people have become more and more used to the vaccines, however, the reporting to VAERS has steadily decreased.
The Vaccine’s Spike Protein:
The Claim:
 Dr. McCullough claims that the “spike protein” produced by the vaccines against COVID-19 are inherently very dangerous since they were originally designed, intentionally, by scientists, as bioweapons. The vaccines cause the body to produce these very same modified spike proteins, which then spread from the site if injection throughout the entire body, wreaking havoc all over the place and resulting in organ damage, infertility, and a high death rate.
Dr. McCullough claims that the “spike protein” produced by the vaccines against COVID-19 are inherently very dangerous since they were originally designed, intentionally, by scientists, as bioweapons. The vaccines cause the body to produce these very same modified spike proteins, which then spread from the site if injection throughout the entire body, wreaking havoc all over the place and resulting in organ damage, infertility, and a high death rate.
Reality:
 This does sound worrisome, except it doesn’t actually happen in reality. In reality, the spike proteins produced according to the coding of the DNA and mRNA vaccine sequences stay local at the site of injection. Only a tiny fraction of the spike proteins ever make it to the bloodstream and most of these are filtered out and destroyed by the liver. They do not “build up” in the adrenal glands, ovaries, lungs, heart, and brains of vaccinated people and can only be detected with the use of highly sensitive equipment. The authors of the papers cited by Dr. McCullough also disagree with his interpretation of their papers. Also, the spike proteins produced by the vaccines are modified so that they simply don’t function the way that the viral spike proteins function. They can’t fold or morph in their shape like the viral spike proteins.
This does sound worrisome, except it doesn’t actually happen in reality. In reality, the spike proteins produced according to the coding of the DNA and mRNA vaccine sequences stay local at the site of injection. Only a tiny fraction of the spike proteins ever make it to the bloodstream and most of these are filtered out and destroyed by the liver. They do not “build up” in the adrenal glands, ovaries, lungs, heart, and brains of vaccinated people and can only be detected with the use of highly sensitive equipment. The authors of the papers cited by Dr. McCullough also disagree with his interpretation of their papers. Also, the spike proteins produced by the vaccines are modified so that they simply don’t function the way that the viral spike proteins function. They can’t fold or morph in their shape like the viral spike proteins.
Now, this isn’t to say that the vaccines against COVID-19 are without any risk whatsoever. As with any vaccine or medical treatment in general, there are always risks. However, for every serious risk that is associated with the vaccines, the very same risk is much much higher when it comes to getting infected by the COVID-19 virus. In fact, getting vaccinated offers substantial protection against numerous key adverse events that are strongly associated with a COVID-19 infection – such as anemia, acute kidney injury, intracranial hemorrhage, lymphopenia, serious blood clots throughout the body, heart damage, brain damage, and especially the risk of death.
The Efficacy of the Vaccines:
The Claim:

Dr. McCullough claims that even if the vaccines were safe, that they just don’t work very well – especially against the Delta Variant. He shows data from Israel, the UK, and the US demonstrating a significant decrease in the effectiveness of the vaccines, over time, when it comes to blocking infection – particularly since the Delta Variant became dominant (June-July of 2021).
Reality:
 Sure, the evidence does show a clear decrease in the effectiveness of the vaccines over time – particularly in response to the Delta Variant of COVID-19. However, what Dr. McCullough fails to mention is that the vaccines have maintained a remarkably high and steady rate of effectiveness against hospitalizations and deaths (greater than 90%). You see, there’s a big difference between completely blocking the COVID-19 virus from infecting the nose and throat of a person (the “nasopharynx”) vs. blocking the virus from invading the bloodstream of a person and spreading throughout the organs of the body. And, since the vaccines are best able to establish a blood-based immunity, it only stands to reason that they would be less effective at blocking a mucosally-based nasopharyngeal infection since this location is not monitored as well by type of immunity that was enhanced or educated to attack the COVID-19 virus via vaccination.
Sure, the evidence does show a clear decrease in the effectiveness of the vaccines over time – particularly in response to the Delta Variant of COVID-19. However, what Dr. McCullough fails to mention is that the vaccines have maintained a remarkably high and steady rate of effectiveness against hospitalizations and deaths (greater than 90%). You see, there’s a big difference between completely blocking the COVID-19 virus from infecting the nose and throat of a person (the “nasopharynx”) vs. blocking the virus from invading the bloodstream of a person and spreading throughout the organs of the body. And, since the vaccines are best able to establish a blood-based immunity, it only stands to reason that they would be less effective at blocking a mucosally-based nasopharyngeal infection since this location is not monitored as well by type of immunity that was enhanced or educated to attack the COVID-19 virus via vaccination.
Vaccines and “Superbugs”:
The Claim:
Dr. McCullough applies a very real fear that is known to happen when antibiotics are overused to argue that the very same thing will happen if vaccines are overused – that they will end up creating “superbugs” that become more and more resistant to vaccines. Instead, it would be much better to not use vaccines and simply find better ways to treat the infections, early during the course of infection, with other medications.
Reality:

Vaccines have long been used to fight various bacterial and viral infections – with great success. Some of the most significant scourges of the past have been completely eradicated with the use of worldwide vaccination programs. The idea, then, that vaccines tend to produce “superbugs” simply hasn’t happened in the past. Why not? Well, because the human immune system is not like antibiotics that tend to target extremely specific regions (known as antigens) on bacteria and viruses. The human immune system is different in that, once it recognizes a “target” on a foreign invader it produces a spectrum of antibodies and T-cell and B-cell receptors against that target as well as to a host of potential variations of this target. This means that if the target mutates or changes over time, the human immune system is already ready for it and will still be able to recognize it despite its mutational changes – most of the time. It’s a very ingenious system, designed by God, to protect us from such infections as well as potential mutational changes over time. It’s not like God was unaware of the potential for antigen mutations when He designed the human immune system.
On top of this, consider that the variants of COVID-19 that have ended up being more infectious and more problematic compared to the original or “wild-type” COVID-19 virus have not come from highly vaccinated regions of the world, but from those regions of the world where vaccination rates are very low. This is only to be expected because mutational changes are greatest where the virus is allowed to infect and multiply the most. So, if you really want to reduce the odds of mutational variations, get vaccinated.
What is also interesting here is that Dr. McCullough is just inconsistent with his idea that the vaccines will somehow produce “superbugs” while his proposed “early treatments” with various medications will not do the same thing. If anything, his own treatment protocol would be more susceptible to this problem since it does not have the advantage of self-modification as the virus mutates.
The Vaccinated vs. the Unvaccinated:
The Claim:
Amazingly, when McCullough, who was asked to comment on the 90-95% of covid patients in the hospital being those who are unvaccinated, claimed that they likely contracted it from the vaccinated. He was blaming the vaccinated for infecting and causing the hospitalizations of the unvaccinated.
Reality:
 Now, while it is true that the Delta Variant has a higher rate of “break-through infections”, as discussed above, and while it is also true that this can result in an infected vaccinated person transmitting the virus to someone else, it is also true that an infected vaccinated person is less infectious and for a shorter amount of time compared to someone who is not vaccinated who gets infected (and who doesn’t already have natural immunity from a previous infection). So, if you want to reduce your risk of infecting someone else who might be even more at risk of a bad outcome, and you don’t already have natural immunity from a previous infection, well, get vaccinated.
Now, while it is true that the Delta Variant has a higher rate of “break-through infections”, as discussed above, and while it is also true that this can result in an infected vaccinated person transmitting the virus to someone else, it is also true that an infected vaccinated person is less infectious and for a shorter amount of time compared to someone who is not vaccinated who gets infected (and who doesn’t already have natural immunity from a previous infection). So, if you want to reduce your risk of infecting someone else who might be even more at risk of a bad outcome, and you don’t already have natural immunity from a previous infection, well, get vaccinated.
Of course, recent evidence also suggests that those who have gained “natural immunity” from a previous infection are even more resistant to the Delta Variant than those who have been vaccinated – and are therefore probably even less likely to transmit the virus to others (Link). And, that is very good news! However, gaining such natural immunity is far more risky compared to getting vaccinated.
The Most Appropriate Christian Response: Link
Early Treatment Protocols:
The Claim:
Dr. McCullough claims that early treatment of a COVID-19 infection is vital and that his early treatment protocol would be able to essentially prevent all hospitalizations (and I suppose all deaths as well), without the need for the “dangerous” vaccinations. Here’s the diagram of Dr. McCullough’s protocol: Link
Reality:
 Do steroids, aspirin, and blood-thinners help those with COVID-19 infections survive? Sure they do. What about monoclonal antibodies like Bamlanivimab, Casirivimab, or Imdevimab? Absolutely beneficial! What about maintaining a good vitamin D level before infection? or perhaps trying to improve one’s vitamin D level early on in infection? Sure, that has some reasonable data support as well (Link). What about vitamin C and zinc along with some Quercitin? I’m more neutral here, but it couldn’t hurt.
Do steroids, aspirin, and blood-thinners help those with COVID-19 infections survive? Sure they do. What about monoclonal antibodies like Bamlanivimab, Casirivimab, or Imdevimab? Absolutely beneficial! What about maintaining a good vitamin D level before infection? or perhaps trying to improve one’s vitamin D level early on in infection? Sure, that has some reasonable data support as well (Link). What about vitamin C and zinc along with some Quercitin? I’m more neutral here, but it couldn’t hurt.
Where I have problems with this “Multidrug Therapy Protocol” is with Dr. McCullough’s recommendation for drugs like hydroxychloroquine and ivermectin. While there was a lot of initial hope that these drugs might work against COVID-19 infections, unfortunately, numerous subsequent scientific studies into this question haven’t shown any useful advantages for these drugs.
When asked about this strong scientific evidence that appears to effectively counter this particular aspect of his early treatment protocol, Dr. McCullough presented the amazing argument that while these drugs may not work when given alone, that they do work in combination with this overall treatment protocol. Of course, he offers no scientific evidence for this or even a suggested mechanism as to how this might be the case. He simply says that it works the way multi-drug programs work against other viral-based diseases – such as the multi-drug protocols that are used to treat HIV infections. What Dr. McCullough fails to explain here is that each individual drug in the HIV protocols has a known beneficial effect, all by itself. This is simply not true of his own early treatment protocol for COVID-19 infections.
So, at this point, it seems clear to me that Dr. McCullough is just being disingenuous in order to save face. After all, he testified early on before the US Senate promoting his early treatment protocol as a means to save the world from the pandemic we’re in – all with minimal cost and without having to worry about masks, social distancing, or vaccines. I’m sure that, after this, he feels that his personal reputation is on the line and it’s just too hard for someone with his inflated ego to admit to an error like this.
Now, it’s not that I’m against early treatment protocols. That’s not it at all. I’m very much a fan of early treatment protocols – as long as they actually work. And, even some of the parts of the protocol used by Dr. McCullough do actually work, as noted above. Other “natural” protocols also have some useful advantages (Link, Link).
The Swiss Cheese Analogy:
To really sum everything up, I’m a fan of the “Swiss Cheese Analogy”. Everyone knows about the holes in a sheet of Swiss cheese. Now, imagine that these layers are bulletproof so that the only way a bullet can get through a layer is if it happens to go through a hole. If all one has available to protect one’s self from getting hit by bullets that are flying all around are sheets of these bulletproof layers of Swiss cheese, what this the best way to protect one’s self from all of the flying bullets? Well, it’s to put as many layers of Swiss cheese around one’s self as is possible.

________________________________________
Bio of Dr. Sean Pitman
 Dr. Sean Pitman is a pathologist, with subspecialties in anatomic, clinical, and hematopathology, currently working in N. California.
Dr. Sean Pitman is a pathologist, with subspecialties in anatomic, clinical, and hematopathology, currently working in N. California.
Vaccines vs. Faith:
Others sin on the right hand. They are much too rash and reckless, tempting God and disregarding everything which might counteract death and the plague. They disdain the use of medicines; they do not avoid places and persons infected by the plague, but lightheartedly make sport of it and wish to prove how independent they are. They say that it is God’s punishment; if he wants to protect them he can do so without medicines or our carefulness. This is not trusting God but tempting him.
.God has created medicines and provided us with intelligence to guard and take good care of the body so that we can live in good health. If one makes no use of intelligence or medicine when he could do so without detriment to his neighbor, such a person injures his body and must beware lest he become a suicide in God’s eyes. . . ..Use medicine; take potions which can help you; fumigate house, yard, and street; shun persons and places wherever your neighbor does not need your presence or has recovered, and act like a man who wants to help put out the burning city. What else is the epidemic but a fire, which instead of consuming wood and straw devours life and body?.You ought to think this way: “Very well, by God’s decree the enemy has sent us poison and deadly offal. Therefore I shall ask God mercifully to protect us. Then I shall fumigate, help purify the air, administer medicine, and take it. I shall avoid places and persons where my presence is not needed in order not to become contaminated and thus perchance infect and pollute others, and so cause their death as a result of my negligence. If God should wish to take me, he will surely find me and I have done what he has expected of me and so I am not responsible for either my own death or the death of others. If my neighbor needs me, however, I shall not avoid place or person but will go freely, as stated above.”..
Personal Note:
Addendum:
The Most Appropriate Christian Response:

 For many, this is a key point of misunderstanding. For example, the well-known Adventist lay evangelist, Scott Ritsema, recently wrote a response to an article published by the Lake Union Herald by Nicholas Miller (Nick is the Lake Union Public Affairs and Religious Liberty director and a professor at the Adventist Theological Seminary at Andrews University). In his response, Scott based pretty much everything on a single concept – the idea that the vaccines against COVID-19, particularly the Delta Variant, do not help to reduce one’s ability to transmit the virus to someone else.
For many, this is a key point of misunderstanding. For example, the well-known Adventist lay evangelist, Scott Ritsema, recently wrote a response to an article published by the Lake Union Herald by Nicholas Miller (Nick is the Lake Union Public Affairs and Religious Liberty director and a professor at the Adventist Theological Seminary at Andrews University). In his response, Scott based pretty much everything on a single concept – the idea that the vaccines against COVID-19, particularly the Delta Variant, do not help to reduce one’s ability to transmit the virus to someone else.
“So, the pivotal question (the only question, really) is, does the vaccine prevent the vaccinated from transmitting the virus?” – Scott Ritsema
Scott’s own answer to this question is that vaccines simply don’t help when it comes to virus transmission.
Now, if Scott is mistaken on this point, and he is actually mistaken here, it would seem that his entire argument crumbles while Nick’s basic position remains credible – i.e., that it would be good for a Christian to get vaccinated since it does reduce the chances of one transmitting the virus to someone else – that it is the loving thing to do for one’s neighbors.
My own position here is that I would much rather convince rather than produce mandates to force vaccinations. In fact, for the most part, I think that such mandates would be counterproductive anyway – with the exception of those working in the medical field taking care of those who are sick or in nursing homes or who are otherwise immunocompromised. But what about limiting unvaccinated people from exposing themselves to many other people in general? – as in large public venues or crowded restaurants? Well, perhaps there is some similarity here to national laws against smoking in public places (as Scott points out himself). Historically, even conservative Adventists like Scott haven’t come out in opposition to such laws against smoking in public places since smoking is generally understood to be unhealthy, not just for the smoker, but for those around the smoker who might be forced to breathe in the “second-hand smoke”. Arguably, while not entirely the same, a somewhat similar situation also exists during a pandemic where an unseen virus can be unknowingly transmitted from a person to other people around him/her through the air. Now, if vaccines are known to reduce the odds of transmitting the virus to someone else, as the current empirical evidence has clearly shown, then these two situations would indeed seem to be similar – not only from a legal perspective, but from a moral perspective as well.
Now, this doesn’t mean that I’m in favor of mandates in general. I’m not. Why not if there is at least some similarity to smoking in public places? Well, I see a key difference that I think is important to consider here. I think that vaccinations are more effective at preventing personal hospitalizations and deaths compared to their effectiveness at reducing viral transmission to others. For me, this means that I favor letting people be free to make up their own minds regarding their own personal risks here – even in public settings. If one believes that the vaccines give him/her significant enough protection against the latest COVID-19 variant, which I do personally believe for myself, then why worry too much about if someone else has or has not been vaccinated? Sure, an important part of the reason why I personally chose to get vaccinated was that I wanted to reduce my chances of spreading the virus to my neighbors as much as possible – to those who might be even more at risk. However, am I willing to enforce this view of mine on others who are opposed to the vaccines? Since vaccines are generally available now for those who want them, I am now, for the most part, not willing to use mandates (with the exception of medical providers as noted above).
Health insurance companies, on the other hand, are likely to raise their rates for those who are unvaccinated since the average cost of a hospital stay for someone sick with COVID-19 is quite high – an average of ~$38,000 (privately insured patient) to ~$73,000 (patient without insurance) (Link) to over $100,000 for an ICU stay, with insurance (Link). The Affordable Care Act allows insurers to charge smokers up to 50% more than what nonsmokers pay for some types of health plans. In 49 states, people who are caught driving without auto insurance face fines, confiscation of their car, loss of their license and even jail. And reckless drivers pay more for insurance (Link). In the same way, insuring the unvaccinated is clearly a greater risk.
For Scott Ritsema’s response (and my reply) see: Link
See also the interesting commentary on this from Martin Luther in his discussion of Faith vs. the Black Death: Link
Reply from Scott Ritsema (8/27/2021):
“
Sean, I’ve re-read your comments this evening, and I have to make a few corrections to your statement quoted above.
First, a minor correction: it’s the head of the CDC’s argument, not mine. More importantly, though, you’ve used a word here – “reduce” – that neither I nor Walenski used, and it changes her statement completely. (I’ll assume this was sloppy of you not sneaky of you.) To be clear for our readers, here’s the argument, her words, not mine: “our vaccines… can’t… prevent transmission.” I think you agree with her on this.
As I write this I wonder what we’re debating, exactly. We are both against mandates, and I think that both of us agree with Walenski that the vaccines are failing to prevent transmission (particularly asymptomatic transmission, which was my addition to the discussion). So that’s all I’ve said. If you’re arguing beyond that, you’re arguing with somebody else, not with me. A smoke-free airplane truly prevents second hand smoke. So, mandatory vaccination and no-smoking are not at all similar; the debate over mandates ends before it begins.
You do have me curious, though. If you’re going to conflate ‘reduce’ and ‘prevent’ I would expect to see evidence that the vaccines are achieving a near-100% reduction in asymptomatic spread among the vaccinated. The link you shared didn’t provide anything on that topic. And Fauci is suggesting otherwise.
“I also think it very unwise to go around promoting the conspiratorial claims of Dr. McCullough – many of which have been shown, by careful scientific investigation, to be either significantly misleading or false. I think this will also end up causing a great deal of harm. Obviously, you believe him rather than someone like me, but time will certainly tell on this one.” – Sean Pitman
Regarding McCullough, as I said in the article, I would’ve loved to have seen the church remain neutral on vaccines. I wouldn’t have gotten involved. When I heard people getting called selfish for declining the vaccine and 100% push for the vaccine on the part of the church, I wanted the other side to be heard also. I think it’s very unwise to try to shut people down and not let them be heard and prevent people from evaluating the claims and evidence on both sides, and deciding for themselves.
My Response:
-
So, if it’s not 100% or “near-100%”, then it’s not helpful? You talk about a “smoke-free airplane” – as in a 100% smoke-free airplane. And, that would be ideal – no question about it. However, what if one could reduce the smoke in the airplane by, say, 50%? Though not “ideal” or “perfect”, wouldn’t that be better than nothing? Clearly, it would be better than nothing – right?
So, for you to argue in absolute terms simply isn’t helpful for your cause. It makes your argument look weak and easily defeatable as long as someone can show at least some benefit to the vaccine when it comes to “reducing” the spread of the virus. And, while certainly well short of being 100% effective, particularly when it comes to the transmission of the Delta Variant, the evidence is quite clear that the vaccines do, in fact, “reduce” viral transmission.
As noted in the article I referenced for you, “While it is also true that this can result in an infected vaccinated person transmitting the virus to someone else, it is also true that an infected vaccinated person is less infectious and for a shorter amount of time compared to someone who is not vaccinated who gets infected.” (Link). Also, please consider the results of the “REACT-1 Study” where the researchers found that “fully vaccinated people in this testing round had between around 50% to 60% reduced risk of infection [Delta Variant], including asymptomatic infection, compared to unvaccinated people. In addition, double vaccinated people were less likely than unvaccinated people to test positive after coming into contact with someone who had COVID-19 (3.84% vs 7.23%).” “Fully vaccinated people who were infected with the virus tended to have less severe illness than unvaccinated people and seemed to have smaller amounts of virus in samples, the researchers added, meaning they may be less likely to pass it on if they are infected.” (Link)
Did you notice the use of the phrase “reduced risk” here? Sure, it’s not 100%, but it’s still significant, when it comes to reducing the odds of spreading the virus to someone else. One becomes less likely to be a link in the chain of transmission if one is vaccinated vs. being unvaccinated (and with no natural immunity from a previous COVID-19 infection).
Given such a situation, it would seem that a good bit of the wind in the sails of your argument disappears. If you build everything upon the concept of 100% equivalence between the vaccinated and the unvaccinated, when it comes to being able to transmit the COVID-19 virus to someone else, then, if this 100% equivalency fails, to even a moderate degree, what happens to your argument? What happens to the conclusion that, perhaps, getting vaccinated would be a loving thing to do for one’s neighbor after all?
As far as Dr. McCullough is concerned, there’s a fundamental difference between “letting people be heard” and actively promoting a particular position. You just don’t come across as a neutral party here who is simply trying to even-handedly present both sides. Rather, you seem to be going well beyond simply letting Dr. McCullough be heard. And, I’m not alone here. I think that most people would see what you’re doing as an active promotion, an endorsement, of Dr. McCullough’s claims – which is a real problem that will result in many more serious injuries and deaths.
Now, I know you don’t see it that way, but if Dr. McCullough is seriously wrong in what he’s saying, and if people take his advice to heart anyway, and end up dead or seriously injured, well, part of that could have been avoided if you hadn’t promoted and apparently endorsed him. I mean, what we do here can have very serious consequences for people.





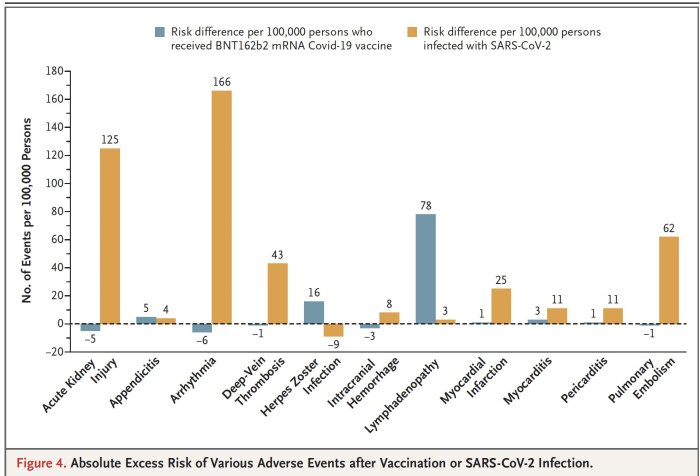









Sean, could you comment on this article?
https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2021-08-21/science-can-t-keep-up-with-virus-creating-worry-for-vaccinated
Bob(Quote)
View CommentI think I covered most if not all of the concerns raised in this article. Which concerns, in particular, do you have?
Sean Pitman(Quote)
View CommentOne part I thought was of interest was:
“For the time being, there are simply more questions than answers. Are breakthrough infections ticking up because of the delta variant, waning immunity or a return to normal life? Are vaccinated people more vulnerable to severe illness than previously thought? Just how common are breakthrough infections? It’s anyone’s guess.
” ‘It is generally the case that we have to make public health decisions based on imperfect data,’ Frieden said. ‘But there is just a lot we don’t know.’ ”
Another article I just read said that it is illegal in most cases for the patient or his doctor to know which variant one has.
Seems kind of crazy.
Bob(Quote)
View CommentWell, I wouldn’t say that it’s “illegal” to know which variant one has, although it may be more difficult to find out – since the rules for labs are “confusing” and it might be somewhat impractical for the CDC to share this information with particular individuals since it takes some time to figure out. However, I’m not sure why this information is being held from public health officials? – at least according to NBC News back in February of 2021? I’m not sure if this situation has improved since then or not?
Right now, at least, one can be pretty confident that if he/she gets sick, it’s with the Delta Variant.
As far as the rate of breakthrough infections and their cause, certainly, our knowledge is incomplete, but it’s also not that bad either. It’s not like the evidence that we currently have gives us no good direction as the basis for decision-making. The degree of breakthrough infections, as well as the relative rate of hospitalizations and deaths, can be determined with a pretty good degree of accuracy. Also, it seems pretty clear that the reason for the increased rate is largely due to the arrival of the Delta Variant, with its significantly increased rate of infection and viral load, along with some decrease in the effectiveness of vaccine-derived immunity over time (particularly beyond 8 months or so. However, the evidence showing a pretty high rate of efficacy against hospitalizations and deaths, for the vaccines, is still very encouraging.
Sean Pitman(Quote)
View CommentThanks for your work. I had a particular interest in the talks given I knew several of the speakers personally. I didn’t get a chance to take notes (making breakfast for the kids), but just off the top of my head I recalled a couple of things about Dr. McCullough’s talk (haven’t gotten to the rest yet). This is probably nit-picking, but I believe Didier Raoult got in trouble for insurance fraud, not just for prescribing hydroxychloroquine as Dr. McCullough implied. His reference to this seemed to get quite a few gasps from the audience. I can’t say he did this solely for sensationalism, but definitely not the whole truth. The more troubling slide was the one on Dr. Mclachlan’s paper on VAERS. His team noted “only 14% of the cases for which a vaccine reaction could be ruled out as a contributing factor in their death.” That’s a far cry from the yellow highlighted heading he added to the article stating “86% of deaths had no other explanation than the vaccine.” How do we know the other 86% had no other explanation? Even the paper’s abstract says only 67% of the cases were reported by medical personnel. This implies that quite a bit were laypersons reporting. The investigators revealed they “found that for at least 13 of the 250 deaths (5%), a vaccine allergic reaction was indisputably the most likely direct cause.” 81% fell in the “other”.
I trust he’s studied this subject much more than I have, but I have to question the motive for this type of reporting other than to garner attention. I never want to needlessly harm a man’s reputation, but sometimes it’s warranted.
This is just me picking things up while flipping pancakes. I can’t imagine what else there is. I pray this issue does not become circumcision 2021 for our church.
Joe Kim(Quote)
View CommentMr. Pitman,
I would love to know how much the pharmaceutical companies are paying you to spread negative alternatives to help ward off these vaccines??? You have said nothing good about anything or anybody that does not agree with you! How sad that you and others are trying so hard to convince everyone that the only route to go is to get the jab. That in itself tells me that I should stay as far away from the jab as I can get!!!
Also, you say that he is “skewing the numbers” of those who have died or been maimed by this vaccine. Well, I truly believe that those in high places have “skewed” the numbers of those who have died from the virus before getting vaccinated. So, who is right??? Two can play that game. Besides, it is not your life that we are talking about.
As far as I am concerned, if one (1) dies or is maimed from this vaccine, it is too many……
LINDA F TAYLOR(Quote)
View CommentI’m sorry you feel that way, but if you think that Dr. McCullough is not “skewing the numbers”, and I am, it might be helpful, to me and to others as well, to provide at least some generally available evidence for this.
As far as saying “nothing good about anything or anybody that does not agree with you”, I did actually point out that I actually agreed with a few of the points that Dr. McCullough presented – in the section called “The Good“. On the other hand, I highly doubt that Dr. McCullough would agree with me on much of anything. Does this make either one of us a “bad person”? It seems to me that such moral judgments should be reserved for God. I personally believe that Dr. McCullough honestly believes what he’s saying. I just think that he is prone to exaggeration and has not been very careful in his investigations or the claims that he’s making – which can result in some serious errors when it comes to correctly interpreting complex data.
As far as the idea that even if the risk of vaccines were extremely rare, such that if “even 1 life” were put at risk in a population of, say, 500 million people, that vaccines should never be considered, seems a bit extreme – given a situation where vaccines have the potential to save the lives of, say, 1% of this population. Are you really suggesting that putting just 1 life at risk is worth the sacrifice of 5 million lives? – given such a situation? I think that, given such a situation, that such a vaccine should most definitely be made available to the population and that the decision to vaccinate should be made by the individual (in most circumstances).
P.S. And no, I don’t get paid for any of this.
Sean Pitman(Quote)
View CommentLinda, I’m not sure singling out Dr. Pittman solves your problem. Roughly 1 million doctors practice in the USA and over 98% are fully vaccinated. But there is a further problem. Your statement, “I would love to know how much the pharmaceutical companies are paying you,” is by proxy a personal insult to over 10 MD’s and nurses in our immediate and extended family whose patient loads are beginning to exceed 50% with the greater numbers being unvacced. At some point, I hope your education will exceed your ignorance in this matter.
Bob Butler(Quote)
View CommentSean, your second Ivermectin link has a problem with it. It should be https://www.salon.com/2021/08/18/ivermectin-studies-analyzed/
Do you know anything about the Jack Lawrence that exposed the problems with the study? Supposedly he’s a masters student in London, had to read the study for a school assignment, and noticed plagiarism in the intro.
Yet at https://grftr.news/why-was-a-major-study-on-ivermectin-for-covid-19-just-retracted/ he writes as if it’s grftr.news that made the discoveries. He’s the founder of grftr.news.
Yet his main target has been Tim Pool, a right-wing American Youtuber, via https://twitter.com/TimPoolClips
How does a guy in Britain just happen to target a right-wing American Youtuber and just happen to expose the problems of an Egyptian medical study? Is he an American studying in London? What does he do for a living? Is Jack Lawrence his real name? How old is he?
I’m not trying to defend the use of Ivermectin, but due to some recent conversations, I thought I’d look into it a little more, and just ended up with some questions.
Bob(Quote)
View CommentI really don’t know anything about Jack Lawrence? I’ll have to look into it…
Sean Pitman(Quote)
View CommentIt may be totally legit, but it comes across to me as fishy.
Masters student in London who likes attacking one single American conservative Youtuber, just happens to notice plagiarism in the study’s intro while reading the study for a class assignment, seemingly has global connections, and all that results in multiple attack articles being published at about the same time. The data set that is supposed to be a major part of the story isn’t readily available, which makes it difficult to substantiate some of the allegations. And to top it off, he is concealing his appearance by using a cat as his profile picture.
To me, it just seems fishy, even if all the allegations against the study are true.
Bob(Quote)
View CommentPerhaps, except that he wasn’t the only one who reviewed the study and found the same problems…
Sean Pitman(Quote)
View CommentThanks for the Interesting and informative breakdown on the talks.
I am still troubled by the idea that we, as Adventists, can do no more than offer a vaccine as a means to combat this, and wonder if that is the sum total of what our health message has become: combat disease through the use of drugs.
Has God given us nothing other than vaccines for this? I find that hard to believe, though I am not against vaccinations, per se.
I saw an interesting article from the NIH regarding the inactivation of the coronavirus:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7112912/
The interesting thing about the article is that the Virus can be deactivated and become non-infective at low pH (1-3) at both 25oC (room temp), and 37oC (slightly elevated body temperature). Putting that together with the fact that pure ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) at 0.03 molar concentration (6 grams/liter) has a pH of about 2.52 indicates that it very well may have value to fight Covid if used properly, as it does have the right pH to inactivate the virus.
Two-time Nobel laureate Linus Pauling claimed that Vitamin C could virtually eliminate the common cold (and probably other viruses). The medical community has said he is/was wrong.
Maybe the medical community ran the tests wrong, and maybe the issue isn’t the concentration you have inside of you but rather the frequency you use it (as a mechanical means of washing away the viral load in one’s mouth and throat)?
Regardless, it seems to me that we should find as many alternatives as possible to offer people a different way to fight this virus for those that feel they in good conscience cannot take it, and for those that feel the risk of the vaccine is greater than they want to accept.
It seems to me we should be the head, and not the tail. We should be working with what God has already given us as much as we can, and make that available in conjunction with the vaccines that are also available.
John B(Quote)
View CommentI’ve been saying all along that the Adventist Health Message has wonderful advantages when it comes to fighting off numerous diseases, including respiratory viruses such as the common cold as well as COVID-19. A great diet, exercise program, religious life, and overall physical and mental health can improve one’s chances of hospital-free survival by more than 80% – and that’s wonderful! However, when it comes to the current pandemic, this just isn’t enough to provide maximum protection – especially as one gets older or has other medical conditions that reduce one’s natural immunity. The mRNA vaccines actually do significantly improve one’s chances of maintaining health and life during this pandemic above and beyond what even the Adventist Health Message can achieve.
On top of this, I’m personally concerned with passing on the virus to others who may be more at risk than I am. The vaccines help to reduce that risk – which I think is very important given that the relative risks of the mRNA vaccines are very low in comparison to the risk of spreading the virus to others.
Sean Pitman(Quote)
View CommentI’m glad you did this Sean because I was getting many requests to do a response and now I can just point them to this.
Steve Lee(Quote)
View CommentThank you Steve! It was great to be part of the panel with you, along with Ivor Myers! (Link) Please do let me know if you have any thoughts or suggestions for improvements.
Sean Pitman(Quote)
View CommentSean, here’s an article which says it’s illegal for most people and their doctors to know which variant they tested positive for:
“You aren’t legally allowed to know which variant gave you COVID-19 in the US, even if it’s Delta”
https://www.businessinsider.com/covid-patients-cant-know-which-variant-infected-them-delta-2021-8
Bob(Quote)
View CommentVery interesting… makes sense.
Sean Pitman(Quote)
View CommentYou mention above that Jack Lawrence wasn’t the only one that called into question that study. That’s what I would expect if something is going on that isn’t quite above board.
Here’s a quote from Jack’s article at https://grftr.news/why-was-a-major-study-on-ivermectin-for-covid-19-just-retracted/ :
“After excluding the data from the Elgazzar study, he found that the effect for ivermectin drops significantly with no discernible effect on severe disease.”
Here’s a meta-analysis: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8088823/
Can you make any sense out of this? How does removing the Elgazzar study change the conclusion? I’ve looked at the various tables, and I just don’t get how Jack could make that statement, or how the person he’s citing could have made that conclusion.
Bob(Quote)
View CommentMeta-analysis studies are heavily dependent upon the most statistically significant study within the overall analysis of multiple studies. That means, of course, that dropping just one study from a meta-analysis can significantly undermine any useful statistical predictive power of the meta-analysis. It’s also another reason why double-blinded placebo-controlled trials are much more reliable – when available.
Sean Pitman(Quote)
View CommentTake a look at the study for yourself, and see if you can substantiate the claim that, “After excluding the data from the Elgazzar study, he found that the effect for ivermectin drops significantly with no discernible effect on severe disease.”
Bob(Quote)
View CommentI have taken a look. And, I find no reason to conclude that this is not the case – as have numerous scientists who have also reviewed this study. This is especially true since this conclusion is supported by a subsequent large double-blinded placebo-controlled study that showed no useful benefits.
Consider again that the “Together Trial” (consisting of nearly 2300 participants in a Phase 3 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial), showed no significant effect on reducing emergency room visits or hospitalizations – despite “early treatment”.
Another smaller double-blinded randomized placebo-controlled trial, involving 476 patients, also failed to show any advantage for ivermectin use (Lopez-Medina, March 4, 2021).
It seems to me that these studies supersede any prior meta-analysis that may have shown some advantages… even if there were no significant problems with these meta-analysis studies.
Sean Pitman(Quote)
View CommentPingback: Dr. Peter McCullough’s COVID-19 and Anti-Vaccine Theories | Detecting Design
“This conclusion is supported by a subsequent large double-blinded placebo-controlled study that showed no useful benefits.”
Can you share a reference for this study? If you are referring to the Together Trial, I believe the sample is much smaller than you have implied for the Ivermectin arm.
Bill(Quote)
View CommentIt seems to me that a scientific study (the Together Trial in this case) involving over 1200 participants (677 in the IVM group & 678 in the Placebo group) in the “ivermectin arm” would be able to yield pretty good predictive value… along with the very same results from another smaller double-blinded randomized placebo-controlled trial, involving 476 people (Lopez-Medina, March 4, 2021). It doesn’t seem very easy to argue against these results.
Sean Pitman(Quote)
View CommentSean, could you please address my question? I didn’t see where you answered it above.
The quote from Jack’s article at https://grftr.news/why-was-a-major-study-on-ivermectin-for-covid-19-just-retracted/ :
“After excluding the data from the Elgazzar study, he found that the effect for ivermectin drops significantly with no discernible effect on severe disease.”
Is that really true?
Here’s a meta-analysis: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8088823/
How does removing the Elgazzar study from this particular meta-analysis change the conclusion? I’ve looked at the various tables, and I just don’t get how Jack could make that statement, or how the person he’s citing could have made that conclusion.
If you think I’m misreading the meta-analysis, please cite or quote the relevant text or table, and explain what I’m overlooking.
I’m not looking for “I don’t see a problem.” I’m looking for, “Look at table X. If you remove the Elgazzar study from that table, the end result is that patients with Y disease receive no benefit at all.”
Above, you cited additional studies rather than addressing the truthfulness of Jack Lawrence’s statement as it pertains to removing the Elgazzar study from the meta-analysis I provided a link to. Those are two different issues.
Whether Jack Lawrence’s key contention is correct or not is essentially irrelevant to my question about his credibility. As far as I’m concerned, I don’t like the idea of taking Ivermectin, but whether one should take it or not is not my concern here.
If a masters student in London, whose hobby is to attack a conservative American Youtuber and who just happens to notice plagiarism in the intro of an Egyptian medical study, is so careless or ignorant as to not see that a claim about a meta-analysis is bogus, then something is dread wrong, and we aren’t being told what is really going on.
Why do I say that? Because the presumed level of astuteness that would lead to the detection of plagiarism would prevent the repeating of a bogus claim about a meta-analysis.
Perhaps the problem is that the meta-analysis I provided the link to wasn’t the same one reanalyzed by the person Lawrence cited. Still, due diligence would require that Lawrence make sure that the claim he’s repeating about meta-analyses is actually sound in the light of other meta-analyses, such as the one I linked to on the NIH website from April 2021.
Bob(Quote)
View CommentI’m sorry, but this isn’t something that interests me given the results of double-blinded placebo-controlled trials that clearly trump meta-analysis studies…
Sean Pitman(Quote)
View CommentCould you explain that? Above you said, “I have taken a look. And, I find no reason to conclude that this is not the case – as have numerous scientists who have also reviewed this study.” That can only mean that you already know what part of the study I’m overlooking. Why would you want to keep that a secret?
“… this isn’t something that interests me ….”
Certainly that can’t mean that you have no interest in making sure your links only go to credible sources.
The two links you gave to show that it doesn’t matter whether Jack Lawrence’s story is on the up and up or not:
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2777389 is only about mild illness, and even admits “larger trials may be needed to understand the effects of ivermectin on other clinically relevant outcomes.” Thus, this study doesn’t refute the entire meta-analysis I linked to, even if this study’s results are reproducible.
https://rethinkingclinicaltrials.org/news/august-6-2021-early-treatment-of-covid-19-with-repurposed-therapies-the-together-adaptive-platform-trial-edward-mills-phd-frcp/ contains no data regarding Ivermectin. But I did find a news article claiming that the results about Ivermectin have not been published or peer reviewed yet.
Any explanation as to why double-blinded RCT’s in Bangladesh, India, Nigeria, presumably Iraq, and Spain would yield different results than the one from Columbia that you linked to? Each of those are listed in the meta-analysis regarding mild illness. (I said presumably Iraq because the meta-analysis called it an RCT, but didn’t include the words double-blinded.)
Perhaps part of the issue is what the Ivermectin was combined with. Comparing Ivermectin with Ivermectin + something else does not prove that Ivermectin isn’t helpful if one of those regimens is less effective than the other.
The news article about the Together Trial decried conspiracy theories. I think a good way to refute conspiracy theories is to show that there aren’t any, by proving that Jack Lawrence is legit. Otherwise, if he’s only a pseudonym, or employed or paid by a drug company, that’s not going to help squelch conspiracy theories.
Bob(Quote)
View CommentI’m sorry. I just don’t agree. The previous DB RCTs that you mention were a lot smaller with much less predictive value. There was a considerable overlap of selected studies in the various reviews and metaanalysis studies – which included pre-printed randomized trials and retrospective cohort studies.
That is probably why larger DB RCTs could not detect a significant advantage…
Sean Pitman(Quote)
View CommentBob, I’ve got to admit, I like your line of questioning. I will add some questions: When one claims that a treatment if ‘effective’ or not – what is the definition of effectiveness? (we can ask that question for COVID treatments AND the vaccine) What is the mechanism by which COVID causes disease – not just the theories, but 1 1/2 years in, do we have a mechanism elucidated? This is important if anyone is going to claim that one treatment is more effective than another. Often the arguments about the effectiveness of treatment choices, such as ivermectin, boil down to a misunderstanding about the purpose of the treatment – and therefore the timing of treatment – which is all about the mechanism. IF one is to look at meta-analysis’s, a big challenge to the usefulness of the data is comparing the methodology of the study and outcome points. It can very well be like comparing apples to oranges. I’d also argue that just because a study is a double blind placebo controlled study, that doesn’t negate data from a meta-analysis – or make that data less powerful. The methodology (and questions asked/answered) matters. So… what is the point of using ivermectin? what is the point of using hydroxychloroquine? What are they trying to do? Would their goal, therefore, depend on timing of use of that medication? For this reason, understanding the ‘process’ of the symptomatology development in COVID is hugely important. At different ‘stages’ of COVID, like other medical issues, treatment choices are and should be different. If I think about mechanisms and stages of the COVID illness, I think there very well may be a place for ivermectin and/or hydroxychloroquine – until the time when good basic science in vitro and in vivo studies suggest otherwise. They are both very safe medications when used properly and are helpful for various types of infections.
I believe I also read in this thread that someone ‘dissed’ vitamins/supplements and their usefulness in treatment of COVID. I think the usefulness of these ‘adjunctive therapies’ is actually based on understanding the mechanisms at the base of our immune responses. I don’t think anyone – including Dr. McCullough – claim that supplements/vitamins/nutrients alone fix COVID. It’s more about understanding that these nutrients are often essential for proper functioning of various enzymes and proteins involved in an immune response…building blocks, if you will. If they are missing, or in short supply – or rapidly being used up due to a very active immune response (for any reason)- then can you have a solid foundation for your immune response to a virus such as COVID? Essentially all of the supplements being recommended to boost the immune system, to ‘prepare’ for potential infection (prophylactic recommendations) or to be used during active treatment are ‘essential’ – our bodies don’t make them. Getting back to the ‘mechanism’ by which COVID causes disease: when might the ‘building blocks’ of our immune response be working overtime? At what point should we be focusing on supporting our immune response? Why might it be helpful to concentrate on supplementing with vitamins/nutrients? Why might believing you get all you need in your food not be a safe option? Is there a way to change that? What risk factors related to those who have the worst outcomes with COVID (and maybe the vaccine??) might be associated with inflammation – and, therefore, perhaps immune system building block issues?
I guess what I’m really getting at is that I think claims that one treatment or another is ‘conspiracy theory’ or ‘effective’ are simply wrong – and happen because of a misunderstanding of goals and not asking the best questions. We should not be polarizing the search for effective treatments. A study supposedly ‘proving’ that ivermectin doesn’t work may very well have a method that set it up to fail (i.e. giving it at a stage in the disease process where it’s MOA isn’t targeting the current problem). Studies that have claimed ivermectin does work need to have their methods reproduced in a study that is a DB RCT… should be easy enough to do given the numbers of COVID cases. Perhaps someone here knows if such a study has been done – so far, I don’t think it has been. I, personally, don’t believe ivermectin or hydroxychloroquin or ANY anti-viral will be very useful by the time someone is very ill – but that’s because I don’t believe the mechanism of illness at that point is actually related to the virus at all. However, early use – maybe preventive use – I don’t think one can make a true scientific conclusion on that yet. And, I think we shoot ourselves in the foot by demonizing these options as ‘conspiracy theories’.
Sunny(Quote)
View CommentIvermectin and hydroxychloroquine have been studied via large RCTs with regard to early treatment and haven’t shown any detectable benefit. The meta-analysis studies were based on numerous low-quality and even a few fraudulent studies that really don’t show good support for any real benefit in light of the larger RCTs.
As far as using vitamins, like vitamin D for instance, you have to have already built up a useful level of vitamin D over the long-term before getting infected by COVID-19 in order to show an advantage. Sure, those with high-normal vitamin D levels do have a survival advantage over those who are vitamin D deficient, given vitamin D in the acute setting after a person is already sick has minimal benefits.
Sean Pitman(Quote)
View CommentSince you did not respond to my principal concern, I think it fairly reasonable to conclude that Jack Lawrence’s statement about the effect of withdrawing the Egyptian study from meta-analyses is at best of questionable accuracy, and at worst a prevarication, since you are unable to show how the withdrawal of that Egyptian study significantly impacts the particular meta-analysis I provided a link to.
And thus, there may really be a conspiracy out there, even if Ivermectin is not an effective treatment.
Bob(Quote)
View CommentOh please. The Elgazzar paper, by itself, accounted for 15.5% of the effect of the meta-analysis paper. Remove that and you basically remove the statistical significance of your meta-analysis paper.
Of the other papers used in the meta-analysis, many relied on small sample sizes or were not randomized or well-controlled. And in 2020, an observational study of the drug was withdrawn after scientists raised concerns about it and a few other papers using data by the company Surgisphere that investigated a range of repurposed drugs against COVID-19. “We’ve seen a pattern of people releasing information that’s not reliable,” says Hill. “It’s hard enough to do work on COVID and treatment without people distorting databases.” (Link).
“I personally have lost all faith in the results of [ivermectin] trials published to date,” says Gideon Meyerowitz-Katz, an epidemiologist at the University of Wollongong in Australia who helped Lawrence to analyze the Elgazzar paper. “It’s not yet possible to assess whether ivermectin works against COVID-19 because the data currently available are not of sufficiently high quality,” he says, adding that he is reading other ivermectin papers in his spare time, looking for signs of fraud or other problems. (Link)
Chaccour and others studying ivermectin say that proof of whether the drug is effective against COVID-19 rests on a handful of large, ongoing studies, including a trial in Brazil with more than 3,500 participants. By the end of 2021, says Zoni, around 33,000 people will have participated in some kind of ivermectin trial. (Link)
And, another recent meta-analysis study by Roman et al., which did not include the Elgazzar study, showed no beneficial effect. (Link)
That’s the reason why larger double-blinded placebo-controlled trials are seen as more reliable, generally speaking, compared to meta-analysis papers – which is why the preliminary results from the large “Together Trial”, and even the smaller Lopez-Medina trial, seem far more convincing to me.
Now, if you want to keep going after possible conspiracies, fine, but that’s not good evidence in support of ivermectin as a useful therapy against COVID-19.
Sean Pitman(Quote)
View CommentNow that the effectiveness of the vaccine is dropping, we have booster shots. Biden and Fauci discussed booster shots every 5 months. Is it safe to pump that much mRNA into a body? Or, is the booster shot different? Notice article about Israel — residents being blocked from entering Sweden.
Epoch Times
Sweden became the second European Union country to ban Israeli residents from entry due to a rise in COVID-19 cases in Israel, despite the country being one of the most vaccinated countries in the world.
Portugal on Wednesday became the first EU country to ban travel from Israel due to a rise in cases. Both countries are following the EU’s recommendation to remove Israel from its list of green countries.
Sweden also banned the entry of citizens from the United States, Kosovo, Lebanon, Montenegro, and North Macedonia.
Interior Minister Mikael Damberg told news outlets that the sharp increases in COVID-19 cases in Israel, the United States, and other countries are the reason why they were removed from Sweden’s travel ban exemption. Despite Israel’s mass vaccination campaign, the virus has continued to spread, Damberg said.
Several Israeli politicians criticized the EU’s directive and Portugal’s mandate.
“Unfortunately, following the EU’s directive, according to which it was decided to remove Israel from the list of green countries, the Portuguese government aligned itself with [the EU’s recommendation] which prohibits entry from Israel to Portugal except for justified reasons,” Itay Mor, the head of Zionist NGO Over The Rainbow Portugal, told YNET.
Interior Minister Mikael Damberg cited the sharp increases in coronavirus infections as the reason the countries were removed from the travel ban exemption, saying that despite Israel’s successful vaccination campaign, the country is still home to large groups of unvaccinated people that have allowed the outbreak to spread.
“We are troubled by this decision, all the more so because most Israelis have been vaccinated. At this stage, the EU should have recognized Israel’s vaccination certificates,” Mor added.
On Aug. 30, the European Union removed the United States, Israel, Kosovo, Lebanon, Montenegro, North Macedonia, and others from its safe travel list. The list is nonbinding and countries are free to determine their own border policies.
“Non-essential travel to the EU from countries or entities not listed in Annex I is subject to temporary travel restriction. This is without prejudice to the possibility for member states to lift the temporary restriction on non-essential travel to the EU for fully vaccinated travelers,” the EU said in a statement at the time.
The United States doesn’t allow European citizens to visit the country freely, despite appeals from the EU. The United States also extended a moratorium on cross-border travel with Canada, as well as Mexico, despite Canada having rescinded travel restrictions for Americans and permanent residents who are fully vaccinated.
Meanwhile, Israel over the weekend announced that individuals who have not received a third booster vaccine shot will not be able to use their vaccine passports.
Even though Israel is one of the most vaccinated countries on Earth against COVID-19, cases are rising. The small nation’s seven-day average for COVID-19 infections on Monday was over 1,000 per one million people, which is double the rate of numbers seen in the United States and the United Kingdom, according to Oxford University’s Our World in Data.
Jody(Quote)
View CommentAs already explained in my article, while Delta cases are risking in Israel, and around the whole world, hospitalizations and death rates are much much lower among the vaccinated as compared to the unvaccinated (within a particular age group). The vaccines even reduce infection rates. The unvaccinated are more than twice as likely to get infected compared to the vaccinated.
You see, the vaccines primarily generate blood-based immunity while the initial Delta infection is a mucosal infection within the nasopharynx. So, while vaccine-based immunity is less effective at blocking the initial Delta infection, it is very good at preventing the virus from spreading from the mucosa of the nasopharynx throughout the rest of the body.
So, it’s not like the vaccines aren’t working. They are working. Additional good news is that natural immunity also appears to be working – but at a high cost (particularly in places like Sweden). Still, a combination of vaccines and natural immunity means that a useful level of “herd immunity” may still be realized this year in Israel and in the US as well.
Sean Pitman(Quote)
View CommentYou did not answer about the booster shots. Please — What Is your opinion about the vaccine given becoming weaker and requiring booster shots? I asked about booster shots — Is it safe to pump that much mRNA into a body? (It appears that booster shots are being proposed yearly — or “every 5 months” as Biden said)
Jody(Quote)
View CommentWhen it comes to severe COVID-19, hospitalizations, and death, booster shots appear to be helpful for those who are over the age of 65 (Link). However, when it comes to those younger than the age of 50, the benefits are not so clear. It seems that for younger people the boosters reduce nasopharyngeal infections, but protection against hospitalizations/death for those who are vaccinated remains high since immune memory (i.e., memory B-cells) remains strong for those who were vaccinated many months ago.
Sean Pitman(Quote)
View Comment“You see, the vaccines primarily generate blood-based immunity while the initial Delta infection is a mucosal infection within the nasopharynx. So, while vaccine-based immunity is less effective at blocking the initial Delta infection, it is very good at preventing the virus from spreading from the mucosa of the nasopharynx throughout the rest of the body.“. Can you provide the data source you use for this statement? It’s my understanding that those getting COVID after vaccination are getting symptoms beyond their nasal mucosa. And, both vaccinated and non- vaccinated are getting similar symptoms (and severity, from my experience). I’m also trying to understand the definition of ‘effectiveness’ ascribed to the vaccine – what definition are you using with relation to the vaccine? From your perspective, does getting Covid give you the same assumed protection as the vaccine? Why/why not? Why should people with antibodies post COVID get the vaccine?
Sunny(Quote)
View CommentThe hospitalization/death rate is far less for the vaccinated vs. the unvaccinated (Link). Note, in this line, that those states with the lowest vaccination rates have the highest death rates per capita:
As far as natural immunity gain via a prior COVID-19 infection, it can actually be superior to the immunity gained via full vaccination. However, natural immunity is less predictable. Up to a third of people who were previously infected by COVID-19 don’t develop antibodies against it (Link). However, if one can demonstrate an adequate level of antibodies against COVID-19 it seems reasonable to me that such people should be considered to have adequate immunity.
As far as the immunity generated by vaccination, the type of immunity generated would not be so effective at preventing a mucosal nasopharyngeal infection since the types of antibodies produced (IgG and IgM) would preferentially be blood-based rather than tissue-based (IgA) type of immunity (Link). Because of this, naturally derived immunity might have an additional advantage in this regard as well.
Sean Pitman(Quote)
View CommentYou say — What Dr. McCullough does not clearly explain is that the mRNA technology and other technologies behind the modern vaccines against the COVID-19 virus (to include the DNA-based vaccines), aren’t exactly “new” or “experimental”. They’ve been around and have been carefully studied now for over 30 years!
I ask — Can you please name the vaccines we got in the past that are mRNA and DNA? Shingles? If around for 30 years, which vaccines are mRNA and DNA . . . so Covid vaccine is not the first given to humans? That’s good to know if true.
Jody(Quote)
View CommentThe mRNA technology has been around for 30+ years – based largely on the work of Katalin Karikó, Ph.D. Moderna was founded in 2010 to produce vaccines based on the new mRNA technology, and the company had been growing as a vaccine manufacturer when the COVID-19 virus became a pandemic early in 2020. BioNTech is a German company established to work on immunotherapies in 2008 by a Turkish couple, who immigrated to Germany. Like Moderna, BioNTech recognized the value of the mRNA technology for vaccine design years ago and licensed the technology. In 2013, BioNTech hired Karikó as a vice president and began to develop mRNA technologies for use against many diseases. BioNTech’s efforts in vaccine development greatly increased in 2018, when Pfizer joined BioNTech’s effort with a research and development agreement to develop mRNA-based vaccines against influenza. It was a natural collaboration because Pfizer, a U.S. company in New York, has been a major vaccine producer for a long time. When the pandemic began, Pfizer/BioNTech immediately turned their attention to developing vaccines against COVID-19. Here’s the details of the story: Link See also: Link
Sean Pitman(Quote)
View CommentSean – You side stepped question. I asked if any mRNA vaccines have been used in the past. You discuss the history of mRNA development but never answer the question if any mRNA vaccines have been used. Now I see from link you posted — “no mRNA vaccine or drug has ever won approval.”
So, this experiment with Covid vaccine is the first mRNA vaccine used on people. FDA approved the vaccine, but the name brand Covid vaccine approved is not available in the U.S. — so everyone is stlll getting EUA vaccine that has “different legal standing” (as FDA explained) — and company cannot be held liable for medical costs of side affects. Only the name (Commodity, or something like that) is FDA approved with “legal standing” that company can be sued for side affects of the vaccine.
So, I’ll answer the questions — Covid is the first mRNA vaccine despite a long history of trying and failing with other mRNA vaccines — and FDA is pulling a trick on Americans by declaring the vaccine “FDA approved” while the company is not providing the FDA approved vaccine to Americans.
Can you not see why people are doubting the vaccine, and doubting your support?
Jody(Quote)
View CommentPfizer’s mRNA vaccine against COVID is now being marketed under the name “Comirnaty” following FDA approval (Link). This isn’t a different vaccine. It’s the very same vaccine.
As far as liability is concerned, again, liability has been taken over by the government so that the vaccines can be made avaiable to everyone. Otherwise, only the rich would be able to afford vaccines.
Sure, this is the first time that mRNA technology has been used to produce a vaccine for the general public. However, it is not the first time that the mRNA technology itself has been successfully used.
So, it isn’t the mRNA technology that is a potential problem. This technology is demonstrably very safe and very effective indeed. The only real question, then, is in regard to the protein product of the vaccine – the “spike protein” in the case of the mRNA vaccines against COVID-19. That’s really the only question here. And, the mRNA vaccines, producing the modified spike protein of COVID-19, have been extensively tested via large double-blinded placebo-controlled trials in both humans and animals – with amazing success regarding efficacy as well as safety. And, these results have continued on now that hundreds of millions of vaccines have been given worldwide. The fact of the matter is that hospital ICUs are currently filling up with those who are very sick and who are dying with COVID-19 (the Delta Variant right now). The significant majority of these people are unvaccinated. These ICUs are not filling up with the vaccinated at all. The vaccines are very clearly highly protective against serious COVID-19 infections. That’s the very clear weight of evidence that we have in hand.
Sean Pitman(Quote)
View CommentI would be interested in your comments on this article from yesterday that this is “not a pandemic of the unvaccinated,” https://www.americanthinker.com/articles/2021/09/is_covid_a_pandemic_of_the_unvaccinated_not_quite.html?fbclid=IwAR2eQ0SEp_PbFRRpKXFOqrUhs9r0TmbCdw15WXki7yHVwgV7AFyLzhRKhoc.
John Fleming(Quote)
View CommentEven with the Delta Variant being prominent since the end of June, those who are vaccinated still have a lower rate of infection and a much lower rate of hospitalization and death – within any given age group. This is true all around the country and around the whole world – even in Israel. So, I would say that yes, this is largely a pandemic of the unvaccinated since the vaccines still do, in fact, provide significant protection. For more details and graphs of this phenomenon see: Link and Link
Sean Pitman(Quote)
View CommentAnother Doctor is presenting the following on Ivermectin, I believe you have studies showing it is not currently effective in reducing COVID infection rates?
Ivermectin works in 6 different ways (mechanisms of action). This is why it is broadly used to treat a variety of conditions in humans and animals. Ivermectin has been used in humans for many decades and is considered one of the safest drugs. The conditions ivermectin used for include: round worm infections, scabies, skin conditions such as rosacea, lupus, etc. Ivermectin trials for corona virus in Bangladesh and China found when combined with zinc and doxycycline has a 100% cure rate for corona viruses. It costs about $2/day to use.
Here are the 6 mechanisms of action (there may be more):
1. ) IVERMECTIN prevents viral entry into host cells. Viruses in general do not have its own machinery to replicate. It makes use of the host cells’ ribosomal complex in order to transcribe and translate its genomic material. And this can only be achieved if the virus gains entry into the host cells.
2) IVERMECTIN prevents viral entry into the nucleus of the cells.
3) IVERMECTIN inhibits genomic transcription and translation.
4) IVERMECTIN prevents cytokine storm.
5) IVERMECTIN prevents CD-147 vascular occlusion and reaching a state of hypercoagulation.
6) IVERMECTIN increases interferon production and enhances its effects. One very important mechanism of immune response against viruses is the production of interferon. Interferon are like the bullets fired directly against the viruses by the immune cells. IVERMECTIN was found to specifically stimulate interferon production and enhancement.
John Fleming(Quote)
View CommentNone of this is true for the level of ivermectin that can actually be tolerated by humans. Also, the best double-blinded placebo-controlled scientific studies haven’t been able to detect any benefit for ivermectin against COVID-19 – much less “100% cure rates”. That’s just plain wrong. Any time someone claims 100% perfection, you need to be very very suspicious of that claim.
Associate Professor Tong says he is aware of a study performed in Bangladesh involving ivermectin. “But it was pretty poor quality, as far as I understand,” he said.
If it were a real effect with such a dramatic result, you would think that much larger double-blinded placebo-controlled trials would have been able to detect the benefit.
Another ivermectin study based in Argentina suggested the deworming pill might’ve prevented 100% of COVID-19 cases. That is, until a recent BuzzFeed News investigation (Link) revealed that at least some of the hospitals named in that study never participated.
Again, none of the larger more controlled and sophisticated trials of ivermectin are finding evidence that the drug helps COVID-19 patients much… which is a problem when it comes to claiming good scientific support, rational support of any kind, for promoting ivermectin as a COVID-19 miracle drug at this point. It just isn’t. The evidence just isn’t there…
Sean Pitman(Quote)
View CommentRumors are rampant, including this video, https://youtu.be/avH5vEgibW0, that the mRNA may trigger an issue with CRSPR, a process that interferes or destroys DNA processes. What would be your response?
John Fleming(Quote)
View CommentThis presentation has so many sensational conspiracy theories in it that it’s hard to decide where to start. It’s all nonsense. The mRNA vaccines have nothing to do with CRSPR and cannot edit one’s DNA or epigenetics controls. Sure, CRSPR could be delivered via mRNA technology (Link), but this has nothing to do with the mRNA vaccines against COVID-19.
There is also no “shedding” from the vaccinated person to any other person. And, “the Japanese study”, mentioned in the video by Dr. Fleming (hopefully no relation to you), deals only with the lipid nanoparticles, not the spike proteins, and only shows that a very tiny fraction of these lipid nanoparticles makes it beyond the injection site to travel to other parts of the body (Link). And, the antibodies produced in vaccinated people against the nucleocapsid as well as the spike protein is due to some vaccinated people having also been infected by the live COVID-19 virus (Link).
Also, this same Dr. Richard Fleming has a history of being convicted of health care, mail, and wire fraud (Link).
He’s just not a credible source on any of the claims he’s making – which are demonstrably false in any case.
Sean Pitman(Quote)
View CommentRumors persist about the COVID vaccines containing secret or proprietary ingredients graphene oxide and fetal cells. What would be your response that the ingredient lists being published are transparent and factual?
John Fleming(Quote)
View CommentI see no evidence that the published ingredient lists for the mRNA vaccines are not transparent and factual. There just is no credible evidence for “graphene” in these vaccines and fetal cell lines simply aren’t necessary to produce these types of vaccines.
Sean Pitman(Quote)
View CommentFetal cell lines were still used in the testing of the vaccines.
midlifestartup(Quote)
View CommentFetal cell lines, originally produced decades ago, were used in the testing of the mRNA vaccines – as they were in the testing of Tylenol, Motrin, Robitussin, Aspirin, Sudafed, Tums, Lidocaine, and a host of other modern medications that most people use on a semiregular basis (Link).
Sean Pitman(Quote)
View CommentPingback: Mandates vs. Religious Exceptions | Educate Truth
Pingback: Mandates vs. Religious Exceptions | Educate Truth
Pingback: Mandates vs. Religious Exceptions | Educate Truth
Pingback: Dr. Robert Malone: From Vaccine Inventor to Conspiracy Theorist? | Educate Truth
Pingback: Dr. Robert Malone: From Vaccine Inventor to Conspiracy Theorist? | Educate Truth
Pingback: Dr. Robert Malone: From Vaccine Inventor to Conspiracy Theorist? | Detecting Design
Pingback: The Pandemic, Vaccination, and the Crisis of Adventist Identity
Pingback: Dr. Aseem Malhotra: From Pro-Vax to Anti-Vax | Educate Truth
Pingback: Dr. Aseem Malhotra: From Pro-Vax to Anti-Vax | Detecting Design
Pingback: Review of “The Naked Emperor” by Pastor Conrad Vine | Educate Truth
Pingback: Dr. John Campbell: mRNA Vaccines Cause Lethal Encephalitis? | Educate Truth